COVID-19 Usurps Host Regulatory Networks
- PMID: 32922297
- PMCID: PMC7456869
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01278
COVID-19 Usurps Host Regulatory Networks
Abstract
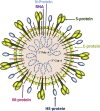
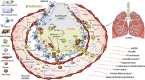
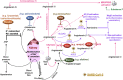
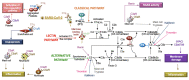
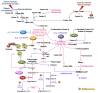
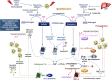
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 binds the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on the cell surface and this complex is internalized. ACE2 serves as an endogenous inhibitor of inflammatory signals associated with four major regulator systems: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), the complement system, the coagulation cascade, and the kallikrein-kinin system (KKS). Understanding the pathophysiological effects of SARS-CoV-2 on these pathways is needed, particularly given the current lack of proven, effective treatments. The vasoconstrictive, prothrombotic and pro-inflammatory conditions induced by SARS-CoV-2 can be ascribed, at least in part, to the activation of these intersecting physiological networks. Moreover, patients with immune deficiencies, hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, and kidney disease often have altered activation of these pathways, either due to underlying disease or to medications, and may be more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Certain characteristic COVID-associated skin, sensory, and central nervous system manifestations may also be linked to viral activation of the RAAS, complement, coagulation, and KKS pathways. Pharmacological interventions that target molecules along these pathways may be useful in mitigating symptoms and preventing organ or tissue damage. While effective anti-viral therapies are critically needed, further study of these pathways may identify effective adjunctive treatments and patients most likely to benefit.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; angiotensin II; bradykinin; coagulation; pharmacotherapy; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; substance P.
Copyright © 2020 Curran, Rivera and Kopp.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

