Rhesus Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Do Not Become Functionally Exhausted in Chronic SIVmac239 Infection
- PMID: 32922404
- PMCID: PMC7457070
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01960
Rhesus Cytomegalovirus-Specific CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Do Not Become Functionally Exhausted in Chronic SIVmac239 Infection
Abstract
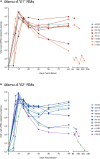
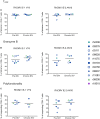
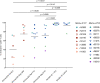
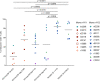
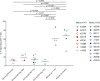
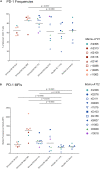
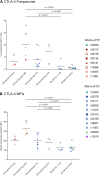
CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) exert potent antiviral activity after HIV/SIV infection. However, efforts to harness the antiviral efficacy of CTLs for HIV/SIV prophylaxis and therapy have been severely hindered by two major problems: viral escape and exhaustion. By contrast, CTLs directed against human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), a ubiquitous chronic herpesvirus, seldom select for escape mutations and remain functional and refractory to exhaustion during chronic HCMV and HIV infection. Recently, attempts have been made to retarget HCMV-specific CTLs for cancer immunotherapy. We speculate that such a strategy may also be beneficial in the context of HIV/SIV infection, facilitating CTL-mediated control of HIV/SIV replication. As a preliminary assessment of the validity of this approach, we investigated the phenotypes and functionality of rhesus CMV (RhCMV)-specific CTLs in SIVmac239-infected Indian rhesus macaques (RMs), a crucial HIV animal model system. We recently identified two immunodominant, Mamu-A∗02-restricted CTL epitopes derived from RhCMV proteins and sought to evaluate the phenotypic and functional characteristics of these CTL populations in chronic SIVmac239 infection. We analyzed and directly compared RhCMV- and SIVmac239-specific CTLs during SIVmac239 infection in a cohort of Mamu-A∗01+ and Mamu-A∗02+ RMs. CTL populations specific for at least one of the RhCMV-derived CTL epitopes were detected in ten of eleven Mamu-A∗02+ animals tested, and both populations were detected in five of these animals. Neither RhCMV-specific CTL population exhibited significant changes in frequency, memory phenotype, granzyme B expression, exhaustion marker (PD-1 and CTLA-4) expression, or polyfunctionality between pre- and chronic SIVmac239 infection timepoints. In chronic SIVmac239 infection, RhCMV-specific CTLs exhibited higher levels of granzyme B expression and polyfunctionality, and lower levels of exhaustion marker expression, than SIVmac239-specific CTLs. Additionally, compared to SIVmac239-specific CTLs, greater proportions of RhCMV-specific CTLs were of the terminally differentiated effector memory phenotype (CD28- CCR7-) during chronic SIVmac239 infection. These results suggest that, in contrast to SIVmac239-specific CTLs, RhCMV-specific CTLs maintain their phenotypes and cytolytic effector functions during chronic SIVmac239 infection, and that retargeting RhCMV-specific CTLs might be a promising SIV immunotherapeutic strategy.
Keywords: cytomegalovirus; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; human immunodeficiency virus; rhesus macaques; simian immunodeficiency virus.
Copyright © 2020 Rosen, Pedreño-Lopez, Ricciardi, Reed, Sacha, Rakasz and Watkins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute-phase innate immune responses in SIVmac239-infected Mamu-B*08+ Indian rhesus macaques may contribute to the establishment of elite control.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1478063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478063. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39502699 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental coinfection of rhesus macaques with rhesus cytomegalovirus and simian immunodeficiency virus: pathogenesis.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(15):7661-71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7661-7671.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12097580 Free PMC article.
-
The Frequency of Vaccine-Induced T-Cell Responses Does Not Predict the Rate of Acquisition after Repeated Intrarectal SIVmac239 Challenges in Mamu-B*08+ Rhesus Macaques.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01626-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01626-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541854 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an effective CTL response against HIV and SIV infections.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:103924. doi: 10.1155/2011/103924. Epub 2011 Sep 29. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21976964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIV infection of rhesus macaques of Chinese origin: a suitable model for HIV infection in humans.Retrovirology. 2013 Aug 15;10:89. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-89. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 23947613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple modes of antigen exposure induce clonotypically diverse epitope-specific CD8+ T cells across multiple tissues in nonhuman primates.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jul 7;18(7):e1010611. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010611. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35797339 Free PMC article.
-
Acute-phase innate immune responses in SIVmac239-infected Mamu-B*08+ Indian rhesus macaques may contribute to the establishment of elite control.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1478063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478063. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39502699 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics analysis of SIV-specific CD8+ T cells in multiple anatomical sites.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 9;20(9):e1012545. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012545. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39250524 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

