Methotrexate Enhances Apoptosis of Transmembrane TNF-Expressing Cells Treated With Anti-TNF Agents
- PMID: 32922407
- PMCID: PMC7456895
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02042
Methotrexate Enhances Apoptosis of Transmembrane TNF-Expressing Cells Treated With Anti-TNF Agents
Abstract
Background: Concomitant use of methotrexate (MTX) improves the clinical efficacy of anti-TNF agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We aimed to clarify the cytotoxic effect of MTX on transmembrane TNF (tmTNF)-expressing cells treated with anti-TNF agents.
Methods: Jurkat T cells stably expressing tmTNF were used for the following experiments. Cytotoxicity induced by an anti-TNF agent (infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol) with concomitant MTX were compared with that by MTX alone or by an anti-TNF agent alone using flow cytometry. Apoptosis-induction mediated by reverse signal through tmTNF, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) were evaluated. Folic acid and Y-27632, a Rho kinase inhibitor, were used as inhibitors to study intracellular signaling pathway in apoptosis induced by MTX and anti-TNF agents.
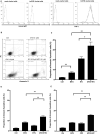
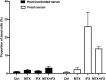
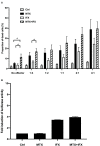
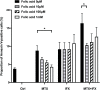
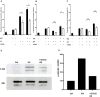
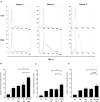
Results: Apoptosis of tmTNF-expressing cells was significantly increased by the concomitant administration of MTX and an anti-TNF agent, compared with MTX alone or an anti-TNF agent alone. The apoptosis induction by concomitant MTX was most pronounced in infliximab-treatment. Reverse signal transduction, but not CDC or ADCC/ADCP, was responsible for the coordinate effect of MTX and an anti-TNF agent on tmTNF-expressing cells. Folic acid inhibited MTX-mediated apoptosis, while Y-27632 suppressed JNK activation and infliximab-induced apoptosis via revere signal through tmTNF.
Conclusion: The apoptotic effect was enhanced by combination of MTX and an anti-TNF agent in tmTNF-expressing cells. The intracellular pathways induced by MTX and anti-TNF agents seem to be independent. These findings might explain at least in part improved the clinical response upon co-therapy of MTX and an anti-TNF agent in RA.
Keywords: anti-TNF agent; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; methotrexate; rheumatoid arthritis; transmembrane TNF.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Oryoji, Mitoma, Kimoto, Koyanagi, Yokoyama, Ayano, Akahoshi, Arinobu, Niiro, Akashi and Horiuchi.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cytotoxic effects of certolizumab pegol and golimumab mediated by transmembrane tumor necrosis factor α.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 May;19(6):1224-31. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e318280b169. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013. PMID: 23619715
-
Mechanisms for cytotoxic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents on transmembrane tumor necrosis factor alpha-expressing cells: comparison among infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 May;58(5):1248-57. doi: 10.1002/art.23447. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18438840
-
The involvement of β-actin in the signaling of transmembrane TNF-α-mediated cytotoxicity.J Leukoc Biol. 2011 Jun;89(6):917-26. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1209812. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21402772
-
Tumor necrosis factors blocking agents: analogies and differences.Acta Biomed. 2012 Apr;83(1):72-80. Acta Biomed. 2012. PMID: 22978063 Review.
-
Tumour necrosis factor α antagonists in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: an immunological perspective.BioDrugs. 2014 Apr;28 Suppl 1:S5-13. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0063-0. BioDrugs. 2014. PMID: 24687234 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Ozoralizumab Administration with or without Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Post-Hoc Analysis.Rheumatol Ther. 2025 Apr;12(2):283-296. doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00737-3. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Rheumatol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39869270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitoma H, Horiuchi T, Tsukamoto H. Binding activities of infliximab and etanercept to transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Gastroenterology. (2004) 126:934–5; author reply 5–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

