Intravascular embolization versus surgical resection for patients with scalp arteriovenous fistula
- PMID: 32922903
- PMCID: PMC7398378
- DOI: 10.1186/s41016-018-0148-1
Intravascular embolization versus surgical resection for patients with scalp arteriovenous fistula
Abstract
Background: Scalp arteriovenous fistula (sAVF) is a rare vascular disease; so far, the standard guidelines for the treatment of sAVF are still unclear. Since its complex vascular anatomical structure, surgical management of sAVF remains an enormous challenge.
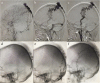
Methods: Between March 2016 and October 2017, three patients with sAVF admitted to the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University were reviewed, and clinical characteristics, imaging features, and surgical outcomes were analyzed.
Results: Three consecutive patients with sAVF were admitted to our hospital during the study period. Two patients received intravascular embolization and one patient received surgical resection. No procedure-related complications occurred after successfully treatment. During the long-term follow-up period, three patients recovered well and had no recurrence of lesion.
Conclusions: Either intravascular embolization or surgical resection is an effective therapy method for sAVF. Careful identification of angioarchitecture features contributes to successful treatment for the complex sAVF; therefore, it is recommended that neurosurgeons make the best treatment plan based on the location and number of the fistulas, feeding the artery, and draining the vein.
Keywords: Intravascular embolization; Scalp arteriovenous fistula; Surgical resection.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

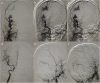
References
-
- Xue B, Yi L, Chao Y. Surgical resection of a complex multiple scalp Avf without preoperative embolization: a case report. Turk Neurosurg. 2015;25:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Cil B, Topcuoglu OM, Peynircioglu B, Arat A, Vargel I. Percutaneous treatment of scalp arteriovenous fistulas by direct puncture and polydocanol sclerotherapy: report of 2 cases with long-term follow-up. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018;28:609–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
