A study of the nonlinear dynamics of human behavior and its digital hardware implementation
- PMID: 32922979
- PMCID: PMC7474202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.006
A study of the nonlinear dynamics of human behavior and its digital hardware implementation
Abstract
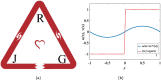
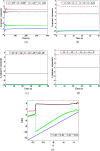
This paper introduces an intensive discussion for the dynamical model of the love triangle in both integer and fractional-order domains. Three different types of nonlinearities soft, hard, and mixed between soft and hard, are used in this study. MATLAB numerical simulations for the different three categories are presented. Also, a discussion for how the kind of personalities affects the behavior of chaotic attractors is introduced. This paper suggests some explanations for the complex love relationships depending on the impact of memory (IoM) principle. Lyapunov exponents, Kaplan-Yorke dimension, and bifurcation diagrams for three different integer-order cases show a significant dependency on system parameters. Hardware digital realization of the system is done using the Xilinx Artix-7 XC7A100T FPGA kit. Version 14.7 from the Xilinx ISE platform is used in both Verilog simulation and hardware implementation stages. The digital approach of such a system opens the door to predict the love relation after sensing the human personality. Also, this study will help in justifying more human emotions like happiness, panic, and fear accurately. Perhaps shortly, this study may combine with artificial intelligence to demonstrate Human-Computer interaction products.
Keywords: Chaos; Chaotic systems; Field programmable gate arrays; Fractional-order systems; Grünwald-Letnikov (GL); Human behavior; Love dynamics; Lyapunov exponents.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Cairo University.
Figures


References
-
- Podlubny I. vol. 198. Elsevier; 1998. (Fractional differential equations: an introduction to fractional derivatives, fractional differential equations, to methods of their solution and some of their applications).
-
- Rudolf H. World Scientific; 2000. Applications of fractional calculus in physics.
-
- Bonilla B., Rivero M., Rodríguez-Germá L., Trujillo J.J. Fractional differential equations as alternative models to nonlinear differential equations. Appl Math Comput. 2007;187(1):79–88.
-
- Elwy O., Abdelaty A., Said L., Radwan A. Fractional calculus definitions, approximations, and engineering applications. J Eng Appl Sci. 2020;67(1):1–30.
-
- Nonlinear Wu.S. information data mining based on time series for fractional differential operators. Chaos: An Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2019;29(1):013114. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

