An Integrated Smartphone-Based Genetic Analyzer for Qualitative and Quantitative Pathogen Detection
- PMID: 32923778
- PMCID: PMC7482303
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02317
An Integrated Smartphone-Based Genetic Analyzer for Qualitative and Quantitative Pathogen Detection
Abstract
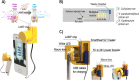
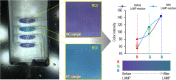
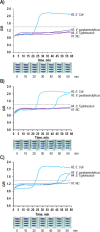
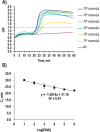
The use of the smartphone is an ideal platform to realize the future point-of-care (POC) diagnostic system. Herein, we propose an integrated smartphone-based genetic analyzer. It consists of a smartphone and an integrated genetic analysis unit (i-Gene), in which the power of the smartphone was utilized for heating the gene amplification reaction, and the camera function was used for imaging the colorimetric change of the reaction for quantitative and multiplex foodborne pathogens. The housing of i-Gene was fabricated by using a 3D printer, which was equipped with a macro lens, white LEDs, a disposable microfluidic chip for loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), a thin-film heater, and a power booster. The i-Gene was installed on the iPhone in alignment with a camera. The LAMP mixture for Eriochrome Black T (EBT) colorimetric detection was injected into the LAMP chip to identify Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The proportional-integral-derivative controller-embedded film heater was powered by a 5.0 V power bank to maintain 63 °C for the LAMP reaction. When the LAMP proceeded, the color was changed from violet to blue, which was real-time monitored by the smartphone complementary metal oxide semiconductor camera. The images were transported to the desktop computer via Wi-Fi. The quantitative LAMP profiles were obtained by plotting the ratio of green/red intensity versus the reaction time. We could identify E. coli O157:H7 with a limit of detection of 101 copies/μL within 60 min. Our proposed smartphone-based genetic analyzer offers a portable, simple, rapid, and cost-effective POC platform for future diagnostic markets.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantification of colorimetric isothermal amplification on the smartphone and its open-source app for point-of-care pathogen detection.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 15;10(1):15123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72095-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32934342 Free PMC article.
-
Centrifugal loop-mediated isothermal amplification microdevice for rapid, multiplex and colorimetric foodborne pathogen detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Jan 15;75:293-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.052. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26322592
-
Point-of-care genetic analysis for multiplex pathogenic bacteria on a fully integrated centrifugal microdevice with a large-volume sample.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Jul 1;136:132-139. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.035. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 31078871
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based microfluidic chip for pathogen detection.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(2):201-224. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1518897. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30569743 Review.
-
Smartphones as mobile microbiological laboratories.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Apr;26(4):421-424. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.09.026. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 31610301 Review.
Cited by
-
Honey bee sHSP are responsive to diverse proteostatic stresses and potentially promising biomarkers of honey bee stress.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 11;11(1):22087. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01547-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34764357 Free PMC article.
-
SMART-LAMP: A Smartphone-Operated Handheld Device for Real-Time Colorimetric Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases via Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;12(6):424. doi: 10.3390/bios12060424. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35735571 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements in Technologies to Detect Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli Shiga Toxins.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 May 28;33(5):559-573. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2212.12025. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36859335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serological and Molecular Detection of Citrus Tristeza Virus: A Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 27;12(8):1539. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081539. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LAMP-Based Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Pathogen Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;12(12):1068. doi: 10.3390/bios12121068. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Food safety; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety.
-
- FDA Food protection plan : an integrated strategy for protecting the nation’s food supply; Food and Drug Administration: 2007.
-
- Park B. H.; Oh S. J.; Jung J. H.; Choi G.; Seo J. H.; Kim D. H.; Lee E. Y.; Seo T. S. An integrated rotary microfluidic system with DNA extraction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and lateral flow strip based detection for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 334–340. 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.063. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

