Phosphorus-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorometric Probes for Iron Detection
- PMID: 32923785
- PMCID: PMC7482302
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02627
Phosphorus-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorometric Probes for Iron Detection
Abstract
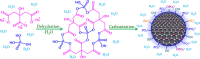
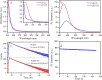
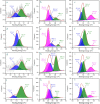
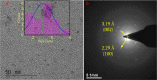
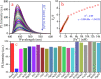
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs), a novel fluorescent nanomaterial, have been extensively employed/explored in various applications, that is, biosensors, bioimaging, nanomedicine, therapeutics, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis, energy storage system, and so forth. In this study, we report the synthesis, characterization, and the application of phosphorus-doped CQDs (PCQDs), synthesized using trisodium citrate and phosphoric acid by the hydrothermal method. The effect of phosphorus doping on optical features and the formation of PCQDs have been explored elaborately by controlling the concentrations of precursors, reaction time, and the temperature. The fluorescent quantum yield for PCQDs was determined to be 16.1% at an excitation/emission wavelength of 310/440 nm. Also, the optical and structural properties of PCQDs were determined by using various spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Static quenching of fluorescence was determined upon the addition of Fe3+ to PCQDs because of the formation of the fluorescent inactive complex (PCQDs-Fe3+). Hence, this chemistry leads to the development of a new fluorometric assay for the detection of Fe3+. The lower limit of Fe3+ detection is determined to be 9.5 nM (3σ/slope), with the linear fit from 20 nM to 3.0 μM (R 2 = 0.99). We have validated this new assay in the raw, ejected, and purified water samples of the RO plant by the standard addition method. These results suggest the possibility of developing a new commercial assay for Fe3+ detection in blood, urine, and various industrial waste and sewage water samples. Furthermore, recycling the pollutant water into the freshwater using filters that consist of PCQDs offers a great deal.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Solvothermal synthesis of phosphorus and nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for iron(III).Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Sep 18;185(10):466. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3002-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30229316
-
A facile green synthesis of functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for a highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 Dec 5;262:120132. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120132. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 34245967
-
Beer-derived nitrogen, phosphorus co-doped carbon quantum dots: Highly selective on-off-on fluorescent probes for the detection of ascorbic acid in fruits.Food Chem. 2023 May 30;409:135243. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135243. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36584525
-
Quantification of 2-chlorohydroquinone based on interaction between N-doped carbon quantum dots probe and photolysis products in fluorescence system.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Mar 25;814:152745. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152745. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34979230
-
High acid-base tolerance and long storage time lanthanum cerium co-doped carbon quantum dots for Fe3+ detection.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025 Feb 15;327:125403. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.125403. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2025. PMID: 39515230
Cited by
-
Effect of Doping Heteroatoms on the Optical Behaviors and Radical Scavenging Properties of Carbon Nanodots.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023 Apr 5;127(15):7360-7370. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c00953. eCollection 2023 Apr 20. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 37113457 Free PMC article.
-
Multicolor Fluorescent Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for Sensing Cancer Cell Biomarkers.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2021 Jan 22;4(1):211-219. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c02526. Epub 2020 Dec 23. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2021. PMID: 34142014 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of yeast cell wall-derived carbon quantum dots with multiple biological activities.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 21;10(9):e29440. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29440. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38699041 Free PMC article.
-
Tagetes erecta as an organic precursor: synthesis of highly fluorescent CQDs for the micromolar tracing of ferric ions in human blood serum.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 3;11(32):19924-19934. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01571k. eCollection 2021 May 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479259 Free PMC article.
-
Water Soluble Silicon Nanoparticles as a Fluorescent Probe for Highly Sensitive Detection of Rutin.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 4;7(32):28588-28596. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03463. eCollection 2022 Aug 16. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35990497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalaiyarasan G.; Joseph J. Determination of Vitamin B12 via PH-Dependent Quenching of the Fluorescence of Nitrogen Doped Carbon Quantum Dots. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3883–3891. 10.1007/s00604-017-2421-y. - DOI
-
- Wang Y.; Hu A. Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. 10.1039/c4tc00988f. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

