Enzyme-Assisted Synthesis of High-Purity, Chain-Deuterated 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- PMID: 32923797
- PMCID: PMC7482301
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02823
Enzyme-Assisted Synthesis of High-Purity, Chain-Deuterated 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Abstract
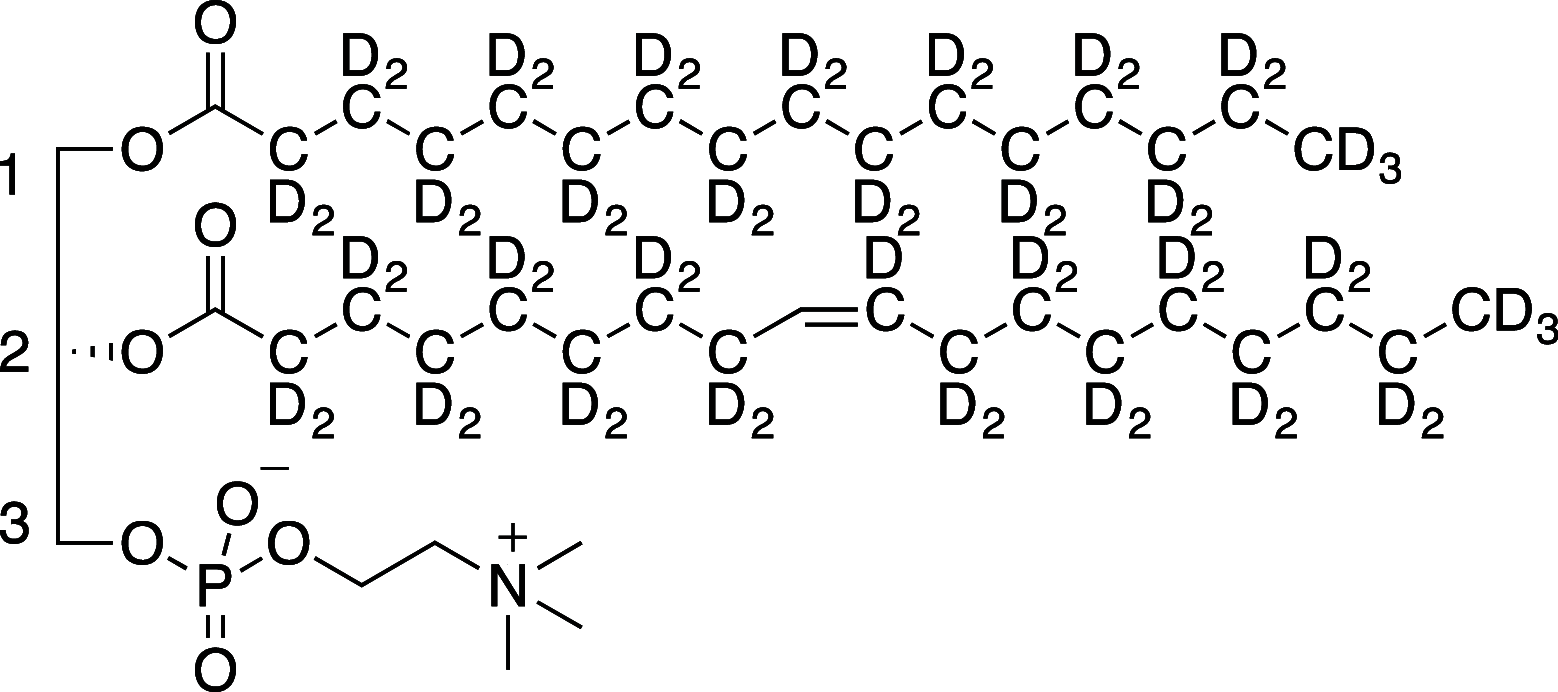
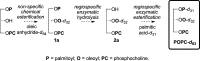
1-Palmitoyl-d 31-2-oleoyl-d 32-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC-d 63) with the palmitoyl and oleoyl chains deuterium-labeled was produced in three steps from 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, deuterated palmitic acid, and deuterated oleic anhydride. Esterification at the sn-2 position was achieved under standard chemical conditions, using DMAP to catalyze the reaction between the 2-lysolipid and oleic anhydride-d 64. Complete regioselective sn-1 acyl substitution was achieved in two steps using operationally simple, enzyme-catalyzed regioselective hydrolysis and esterification to substitute the sn-1 chain for a perdeuterated analogue. This method provides chain-deuterated POPC with high chemical purity (>96%) and complete regiopurity, useful for a variety of experimental techniques. This chemoenzymatic semisynthetic approach is a general, modular method of producing highly pure, mixed-acyl phospholipids, where the advantages of both chemical synthesis (efficiency, high yields) and biocatalytic synthesis (specificity, nontoxicity) are realized.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of Perdeuterated 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine ([D82 ]POPC) and Characterisation of Its Lipid Bilayer Membrane Structure by Neutron Reflectometry.Chempluschem. 2016 Mar;81(3):315-321. doi: 10.1002/cplu.201500452. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Chempluschem. 2016. PMID: 31968790
-
Thermal and 13C-NMR study of the dynamic structure of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine and 1-oleyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in aqueous dispersions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 7;687(2):231-7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90551-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982. PMID: 7093254
-
Effects of specific fatty acid acylation of phospholipase A2 on its interfacial binding and catalysis.Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 27;33(38):11598-607. doi: 10.1021/bi00204a022. Biochemistry. 1994. PMID: 7918373
-
Synthesis of deuterated [D32 ]oleic acid and its phospholipid derivative [D64 ]dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013 Jul-Aug;56(9-10):520-9. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3088. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 24285531
-
Pressure effect on the bilayer phase transition of asymmetric lipids with an unsaturated acyl chain.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Feb;1189:77-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05203.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20233371
Cited by
-
New Insights into the Interaction of Class II Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenases with Ubiquinone in Lipid Bilayers as a Function of Lipid Composition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 23;23(5):2437. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052437. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269583 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical cobalt-catalyzed semi-deuteration of alkynes to access deuterated Z-alkenes.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 10;16(1):2390. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57782-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40064911 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

