Activity of the Highly Specific RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) in Pediatric Patients With Tumors Harboring RET Gene Alterations
- PMID: 32923911
- PMCID: PMC7450975
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.19.00401
Activity of the Highly Specific RET Inhibitor Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) in Pediatric Patients With Tumors Harboring RET Gene Alterations
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center. Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (Open Payments). Sandya Govinda RajuEmployment: Loxo OncologyDahlia HenryEmployment: Loxo Oncology Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Loxo Oncology, Allergan, Axovant Sciences, Palatin TechnologiesSteve SmithConsulting or Advisory Role: Various, Loxo Oncology Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Various patents and applications Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: VariousS. Michael RothenbergEmployment: Loxo Oncology Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Loxo OncologyMichael C. CoxEmployment: Bayer, Loxo Oncology, Merck KGaA, Amgen, Day One Biopharmaceuticals Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Loxo Oncology, Bayer, Merck KGaA, Amgen, Day One Biopharmaceuticals Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: US patent 62/318,041 issued to Loxo Oncology (Inst)Julia Glade BenderConsulting or Advisory Role: AbbVie (Inst) Research Funding: Celgene (Inst), Merck (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Ignyta (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Eisai (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Eli Lilly (Inst), Loxo Oncology (Inst), Genentech (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, Amgen, Merck, Bayer, Genentech Uncompensated Relationships: SpringWorks Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers SquibbA. Lindsay FrazierStock and Other Ownership Interests: Decibel Therapeutics Consulting or Advisory Role: Decibel TherapeuticsPeter AndersonStock and Other Ownership Interests: Healios Consulting or Advisory Role: Enlivity Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Patent for glutamine and trehalose compositions; priority date 13 September 2013; App 14/470, 545, filed August 27, 2014; patent 61/878,084 issued December 26, 2017 Other Relationship: EnlivityAlberto S. PappoHonoraria: Bayer, Roche Consulting or Advisory Role: Merck, Loxo Oncology/Bayer, EUSA Pharma No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
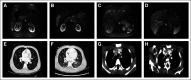
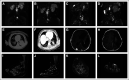
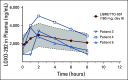
Similar articles
-
The L730V/I RET roof mutations display different activities toward pralsetinib and selpercatinib.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021 Jun 7;5(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s41698-021-00188-x. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34099825 Free PMC article.
-
Selpercatinib: First Approval.Drugs. 2020 Jul;80(11):1119-1124. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01343-7. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32557397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic and CNS Activity of Selective RET Inhibition With Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) in a Patient With RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer With Extensive CNS Metastases.JCO Precis Oncol. 2020 Oct 30;4:PO.20.00096. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00096. eCollection 2020. JCO Precis Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33154983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Decade in review: a new era for RET-rearranged lung cancers.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;9(6):2571-2580. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-346. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33489819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 27;383(9):813-824. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005653. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32846060 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Improving Global Access to Genomic Profiling in Rare Pediatric Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 1;31(15):3285-3295. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-3910. Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40392980
-
Fusion Oncogenes Are Associated With Increased Metastatic Capacity and Persistent Disease in Pediatric Thyroid Cancers.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Apr 1;40(10):1081-1090. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01861. Epub 2022 Jan 11. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35015563 Free PMC article.
-
Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Towards a Precision Medicine.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 29;13:864253. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.864253. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35422765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracranial Activity of Selpercatinib in Chinese Patients With Advanced RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the Phase II LIBRETTO-321 Trial.JCO Precis Oncol. 2023 Jun;7:e2200708. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00708. JCO Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37315261 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting the RET tyrosine kinase in neuroblastoma: A review and application of a novel selective drug design strategy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;216:115751. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115751. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37595672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kato S, Subbiah V, Marchlik E, et al. RET aberrations in diverse cancers: Next-generation sequencing of 4,871 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:1988–1997. - PubMed
-
- Ceccherini I, Pasini B, Pacini F, et al. Somatic in frame deletions not involving juxtamembranous cysteine residues strongly activate the RET proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1997;14:2609–2612. - PubMed
-
- Prescott JD, Zeiger MA. The RET oncogene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer. 2015;121:2137–2146. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara R, Auger N, Auclin E, et al. Clinical and translational implications of RET rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13:27–45. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

