Endothelial connexins in vascular function
- PMID: 32923963
- PMCID: PMC7439941
- DOI: 10.1530/VB-19-0015
Endothelial connexins in vascular function
Abstract
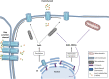
Gap junctions are essential for intercellular crosstalk in blood and lymphatic vasculature. These clusters of intercellular channels ensure direct communication among endothelial cells and between endothelial and smooth muscle cells, and the synchronization of their behavior along the vascular tree. Gap junction channels are formed by connexins; six connexins form a connexon or hemichannel and the docking of two connexons result in a full gap junction channel allowing for the exchange of ions and small metabolites between neighboring cells. Recent evidence indicates that the intracellular domains of connexins may also function as an interaction platform (interactome) for other proteins, thereby regulating their function. Interestingly, fragments of Cx proteins generated by alternative internal translation were recently described, although their functions in the vascular wall remain to be uncovered. Variations in connexin expression are observed along different types of blood and lymphatic vessels; the most commonly found endothelial connexins are Cx37, Cx40, Cx43 and Cx47. Physiological studies on connexin-knockout mice demonstrated the essential roles of these channel-forming proteins in the coordination of vasomotor activity, endothelial permeability and inflammation, angiogenesis and in the maintenance of fluid balance in the body.
Keywords: connexin; endothelium; gap junction; intercellular communication.
© 2019 The authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexins in vascular physiology and pathology.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009 Feb;11(2):267-82. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2115. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009. PMID: 18834327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow regulates intercellular communication in HAEC by assembling functional Cx40 and Cx37 gap junctional channels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):H2015-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00204.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16361362
-
Connexins in the control of vasomotor function.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019 Jan;225(1):e13108. doi: 10.1111/apha.13108. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 29858558 Review.
-
Heterogeneous expression of endothelial connexin (Cx) 37, Cx40, and Cx43 in rat large veins.Anat Sci Int. 2009 Sep;84(3):237-45. doi: 10.1007/s12565-009-0029-y. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Anat Sci Int. 2009. PMID: 19322632
-
Expression pattern of connexin gene products at the early developmental stages of the mouse cardiovascular system.Circ Res. 1997 Sep;81(3):423-37. doi: 10.1161/01.res.81.3.423. Circ Res. 1997. PMID: 9285645
Cited by
-
Connexins Signatures of the Neurovascular Unit and Their Physio-Pathological Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 23;23(17):9510. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179510. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell communication and relevant signaling pathways in osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling.Bone Res. 2025 Apr 7;13(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00417-0. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40195313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescent Endothelial Cells in Cerebral Microcirculation Are Key Drivers of Age-Related Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Microvascular Rarefaction, and Neurovascular Coupling Impairment in Mice.Aging Cell. 2025 Jul;24(7):e70048. doi: 10.1111/acel.70048. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 40167015 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Endothelial Connexin37 Reduces Angiogenesis and Decreases Tumor Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 8;23(6):2930. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062930. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328350 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and Functional Remodeling of Vascular Endothelium in Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 19;24(3):1998. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031998. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

