Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether-induced testicular oxidative stress and time-dependent up-regulation of apoptotic, pro-inflammatory, and oncogenic markers in rats
- PMID: 32924002
- PMCID: PMC7451700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100051
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether-induced testicular oxidative stress and time-dependent up-regulation of apoptotic, pro-inflammatory, and oncogenic markers in rats
Abstract
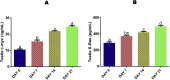
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (EGME) is a major component of paints, lacquers, inks, and automobile brake fluids. As a result, exposures to humans are inevitable. We therefore, investigated in this study, its effect on testicular cells in a time-course manner in male Wistar rats. Animals were orally administered 50 mg/kg body weight of EGME for duration of 7, 14, and 21 days. Following 7 days of the administration, levels of NO and GSH were significantly reduced, while levels of c-Myc, K-Ras, caspase-3, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β were significantly increased compared with control. At the end of 14 days exposure, GPx, and SOD activities, as well as IL-10 level were significantly decreased, while levels of c-Myc, K-Ras, p53, Bax, caspase-3, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, and GST activity were significantly elevated compared with control. After 21 days of EGME administration, Bcl-2, IL-10, and NO levels were significantly decreased, while levels of c-Myc, K-Ras, p53, Bax, caspase-3, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, MDA and GST activity were significantly increased compared with control. After 7, 14, and 21 days of EGME administrations, testis histopathology showed severe loss of seminiferous tubules, the seminiferous epithelium revealed very few spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatogonia, spermatozoa, and Sertoli cells, while the interstitial tissue is eroded, with scanty abnormal Leydig cells, compared with the control that appeared normal. We therefore, concluded that EGME-induced testicular toxicity as a result of EGME administration could be via the disorganization of the endogenous antioxidant systems as well as up-regulation of pro-inflammatory, apoptotic and oncogenic mediators in rats.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bax, Bcl-2 associated X; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CAT, catalase; Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GST, glutathione S-transferase; Histopathology; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; Inflammation; K-Ras, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene; MDA, malondialdehyde; NO, nitric oxide; Oncogenes; Oxidative stress; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; Testis; c-Myc, myelocytomatosis; p53, tumor suppressor protein.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress-mediated induction of pulmonary oncogenes, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers following time-course exposure to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in rats.Metabol Open. 2020 Dec 15;9:100075. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100075. eCollection 2021 Mar. Metabol Open. 2020. PMID: 33409483 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl cellosolve-induced renal oxidative stress and time-dependent up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptotic, and oncogenic markers in rats.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Jun 23;7:779-787. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.007. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32642444 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic oxidative stress, up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptotic and oncogenic markers following 2-methoxyethanol administrations in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Aug 29;24:100806. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100806. eCollection 2020 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32913901 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether: impact on testicular gene expression.Int J Androl. 2008 Apr;31(2):269-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00846.x. Epub 2007 Dec 30. Int J Androl. 2008. PMID: 18179559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview on the protective effects of ellagic acid against heavy metals, drugs, and chemicals.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Sep 26;11(12):7469-7484. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3704. eCollection 2023 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38107104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Moringa oleifera Extract Extenuates Echis ocellatus Venom-Induced Toxicities, Histopathological Impairments and Inflammation via Enhancement of Nrf2 Expression in Rats.Pathophysiology. 2021 Mar 5;28(1):98-115. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology28010009. Pathophysiology. 2021. PMID: 35366273 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic acid demonstrates an anti-inflammatory effect via modulation of the NF-κB-iNOS-COX-2 and JAK-STAT signaling pathways in methyl cellosolve-induced hepato-testicular inflammation in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 May 5;34:101484. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101484. eCollection 2023 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37197735 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as promising testicular translatable safety biomarkers: current state and future perspectives.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Apr;97(4):947-961. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03460-0. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36795116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress-mediated induction of pulmonary oncogenes, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers following time-course exposure to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in rats.Metabol Open. 2020 Dec 15;9:100075. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2020.100075. eCollection 2021 Mar. Metabol Open. 2020. PMID: 33409483 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of syringic acid on steroid and gonadotropic hormones, hematological indices, sperm characteristics and morphologies, and markers of tissue damage in methyl cellosolve-administered rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Oct 7;32:101360. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101360. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36237443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takei M., Ando Y., Saitoh W., Tanimoto T., Kiyosawa N., Manabe S., Sanbuissho A., Okazaki O., Iwabuchi H., Yamoto T., Adam K.P., Weiel J.E., Ryals J.A., Milburn M.V., Guo L. Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether–induced toxicity is mediated through the inhibition of flavoprotein dehydrogenase enzyme family. Toxicol Sci. 2010;118(2):643–652. - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Ketttenis P. The historic and current use of glycol ethers: a picture of change. Toxicol Lett. 2005;156:5–11. - PubMed
-
- Boatman R.J. International industry initiatives to improve the glycol ether health effects knowledge base. Toxicol Lett. 2005;156:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Johanson G. Toxicity review of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and its acetate ester. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000;30:307–345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

