B-Cell-Targeted 3DNA Nanotherapy Against Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) Ameliorates Autoimmune Arthritis in a Preclinical Model
- PMID: 32924009
- PMCID: PMC7457693
- DOI: 10.1177/2632010X20951812
B-Cell-Targeted 3DNA Nanotherapy Against Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) Ameliorates Autoimmune Arthritis in a Preclinical Model
Abstract
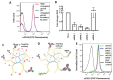
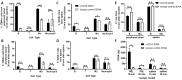
The tryptophan catabolizing enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) has been identified as an immunomodulatory agent promoting autoimmunity in preclinical models. As such, finding ways to target the expression of IDO2 in B cells promises a new avenue for therapy for debilitating autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. IDO2, like many drivers of disease, is an intracellular protein expressed in a range of cells, and thus therapeutic inhibition of IDO2 requires a mechanism for targeting this intracellular protein in specific cell types. DNA nanostructures are a promising novel way of delivering small molecule drugs, antibodies, or siRNAs to the cytoplasm of a cell. These soluble, branched structures can carry cell-specific targeting moieties along with their therapeutic deliverable. Here, we examined a 3DNA nanocarrier specifically targeted to B cells with an anti-CD19 antibody. We find that this 3DNA is successfully delivered to and internalized in B cells. To test whether these nanostructures can deliver an efficacious therapeutic dose to alter autoimmune responses, a modified anti-IDO2 siRNA was attached to B-cell-directed 3DNA nanocarriers and tested in an established preclinical model of autoimmune arthritis, KRN.g7. The anti-IDO2 3DNA formulation ameliorates arthritis in this system, delaying the onset of joint swelling and reducing total arthritis severity. As such, a 3DNA nanocarrier system shows promise for delivery of targeted, specific, low-dose therapy for autoimmune disease.
Keywords: 3DNA; IDO2; arthritis; autoimmunity; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: J.B. is Director of Academic Collaborations and Marketing Communications, T.S. is a Research and Development Scientist, and R.G. is Founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Genisphere LLC, the commercial manufacturer of 3DNA. L.M.-N. and L.M.F.M. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of IDO1 and IDO2 on the B Cell Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 13;13:886225. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886225. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35493480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic antibody targeting of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO2) inhibits autoimmune arthritis.Clin Immunol. 2017 Jun;179:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.01.016. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28223071 Free PMC article.
-
IDO2: A Pathogenic Mediator of Inflammatory Autoimmunity.Clin Med Insights Pathol. 2016 Nov 21;9(Suppl 1):21-28. doi: 10.4137/CPath.S39930. eCollection 2016. Clin Med Insights Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27891058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IDO2 Drives Autoantibody Production and Joint Inflammation in a Preclinical Model of Arthritis by Repressing Runx1 Function in B Cells.J Immunol. 2024 Dec 1;213(11):1595-1604. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400445. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39400244
-
IDO2 is a critical mediator of autoantibody production and inflammatory pathogenesis in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 1;192(5):2082-2090. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303012. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24489090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Immunomodulatory Enzyme IDO2 Mediates Autoimmune Arthritis through a Nonenzymatic Mechanism.J Immunol. 2022 Feb 1;208(3):571-581. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100705. Epub 2021 Dec 29. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34965962 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of IDO1 and IDO2 on the B Cell Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 13;13:886225. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886225. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35493480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limited nutrient availability in the tumor microenvironment renders pancreatic tumors sensitive to allosteric IDH1 inhibitors.Nat Cancer. 2022 Jul;3(7):852-865. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00393-y. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Nat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35681100 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-based nanotherapeutics as emerging modalities for immune-mediated diseases: A preliminary review.Cell Biol Int. 2022 Sep;46(9):1320-1344. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11841. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Cell Biol Int. 2022. PMID: 35830711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Kynurenine Pathway-New Linkage between Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Autoimmune Endocrinopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 13;22(18):9879. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189879. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayter SM, Cook MC. Updated assessment of the prevalence, spectrum and case definition of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:754-765. - PubMed
-
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:15-25. - PubMed
-
- Gibofsky A. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: a synopsis. Am J Manag Care. 2014;20:S128-S135. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

