Contemporary Incidence and Prevalence of Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in Australia Using Linked Data: The Case for Policy Change
- PMID: 32924748
- PMCID: PMC7792417
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016851
Contemporary Incidence and Prevalence of Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in Australia Using Linked Data: The Case for Policy Change
Abstract
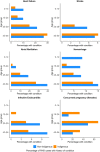
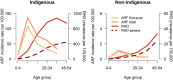
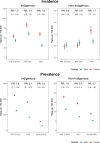
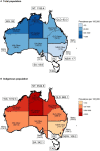
Background In 2018, the World Health Organization prioritized control of acute rheumatic fever (ARF) and rheumatic heart disease (RHD), including disease surveillance. We developed strategies for estimating contemporary ARF/RHD incidence and prevalence in Australia (2015-2017) by age group, sex, and region for Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians based on innovative, direct methods. Methods and Results This population-based study used linked administrative data from 5 Australian jurisdictions. A cohort of ARF (age <45 years) and RHD cases (<55 years) were sourced from jurisdictional ARF/RHD registers, surgical registries, and inpatient data. We developed robust methods for epidemiologic case ascertainment for ARF/RHD. We calculated age-specific and age-standardized incidence and prevalence. Age-standardized rate and prevalence ratios compared disease burden between demographic subgroups. Of 1425 ARF episodes, 72.1% were first-ever, 88.8% in Indigenous people and 78.6% were aged <25 years. The age-standardized ARF first-ever rates were 71.9 and 0.60/100 000 for Indigenous and non-Indigenous populations, respectively (age-standardized rate ratio=124.1; 95% CI, 105.2-146.3). The 2017 Global Burden of Disease RHD prevalent counts for Australia (<55 years) underestimate the burden (1518 versus 6156 Australia-wide extrapolated from our study). The Indigenous age-standardized RHD prevalence (666.3/100 000) was 61.4 times higher (95% CI, 59.3-63.5) than non-Indigenous (10.9/100 000). Female RHD prevalence was double that in males. Regions in northern Australia had the highest rates. Conclusions This study provides the most accurate estimates to date of Australian ARF and RHD rates. The high Indigenous burden necessitates urgent government action. Findings suggest RHD may be underestimated in many high-resource settings. The linked data methods outlined here have potential for global applicability.
Keywords: Australia; epidemiology; ethnic; inequalities; linked data; rheumatic heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Seventy‐First World Health Assembly A71/25. Resolution adopted on 25 May 2018 for provisional agenda 12.8 by Director General on 12 April 2018. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- Watkins DA, Johnson CO, Colquhoun SM, Karthikeyan G, Beaton A, Bukhman G, Faorousanfar MH, Longnecker CT, Mayosi BM, Mensah GA, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatic heart disease, 1990–2015. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, Steer AC, Mulholland EK, Weber M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:685–694. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan E. Global assessment of rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease at the close of the century. Circulation. 1993;88:1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

