Lung Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Pediatric COVID-19: A Case Series
- PMID: 32925701
- PMCID: PMC7497604
- DOI: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000002254
Lung Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Pediatric COVID-19: A Case Series
Abstract
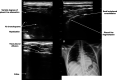
Lung point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) has been shown to be useful for identifying pulmonary pathology in adult patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, pediatric literature for POCUS in COVID-19 is limited. The objective of this case series was to describe lung POCUS findings in pediatric patients with COVID-19. Three patients with COVID-19 who had lung POCUS performed in a pediatric emergency department were included. Point-of-care ultrasound revealed bilateral abnormalities in all patients, including pleural line irregularities, scattered and coalescing B-lines, consolidations, and pleural effusions. Additional pediatric studies are necessary to gain a broader understanding of COVID-19's sonographic appearance in this age group and to determine whether POCUS may be helpful to facilitate diagnosis and expedite management decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American College of Emergency Physicians ACEP guideline on COVID-19: ultrasound machine and transducer cleaning. Available at: https://www.acep.org/globalassets/new-pdfs/guideline-on-covid-19--ultras.... Accessed July 20, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang Y Wang S Liu Y, et al. . A preliminary study on the ultrasonic manifestations of peripulmonary lesions of non-critical novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Available at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3544750. Accessed May 5th, 2020.
-
- Buonsenso D Piano A Raffaelli F, et al. . Point-of-care lung ultrasound findings in novel coronavirus disease-19 pneumoniae: a case report and potential applications during COVID-19 outbreak. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:2776–2780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

