S100A4 Silencing Facilitates Corneal Wound Healing After Alkali Burns by Promoting Autophagy via Blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 32926102
- PMCID: PMC7490227
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.61.11.19
S100A4 Silencing Facilitates Corneal Wound Healing After Alkali Burns by Promoting Autophagy via Blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum in: S100A4 Silencing Facilitates Corneal Wound Healing After Alkali Burns by Promoting Autophagy via Blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Mar 1;62(3):19. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.3.19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33720275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
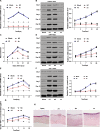
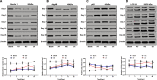
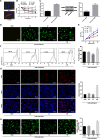
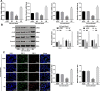
Purpose: This study investigated the role of S100 calcium binding protein A4 (S100A4) in corneal wound healing and the underlying mechanism of the S100A4-mediated PI3K/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway.
Methods: The rabbit corneal alkali burn model was established in vivo. S100A4 expression, wound healing, inflammation, and autophagy in rabbit cornea after alkali burn were detected. The NaOH-treated rabbit corneal stromal cells (rCSCs) were transfected with overexpressed S100A4 or silencing S100A4 to examine the effect of S100A4 on corneal wound healing in vitro. The effect of S100A4 on cell viability, proliferation, migration, invasion, fibrosis, and autophagy of rCSCs after alkali burn was analyzed. Then the functional rescue experiments were carried out. The PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, was used to elucidate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in rCSCs.
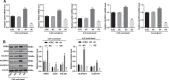
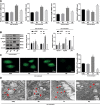
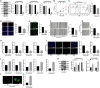
Results: S100A4 silencing promoted rabbit corneal wound healing by inhibiting fibrosis and inflammation and promoting autophagy in alkali-burned cornea, corresponding to increased levels of LC3, Beclin 1, and Atg4B but lowered α-smooth muscle actin, TNF-ɑ, and p62 levels. Moreover, silencing S100A4 inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and fibrosis of NaOH-treated rCSCs and promoted the differentiation of rCSCs into corneal cells and the autophagy of damaged rCSCs. The inhibitory role of S100A4 in wound healing was achieved via activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Conclusions: S100A4 silencing confers a promising effect on wound healing of alkali-burned cornea by blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, supporting the advancement of corneal gene therapies for wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of S100A4 gene silencing on alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization: an in vivo study.Mol Vis. 2017 Apr 26;23:286-295. eCollection 2017. Mol Vis. 2017. PMID: 28479848 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin ameliorates corneal injury after alkali burn through methylation modification in mouse TSC1 and mTOR genes.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Feb;203:108399. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108399. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33352197
-
Analysis of Smad3 in the modulation of stromal extracellular matrix proteins in corneal scarring after alkali injury.Mol Vis. 2024 Dec 30;30:448-464. eCollection 2024. Mol Vis. 2024. PMID: 39959170 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting PI3K/mTOR signaling to accelerate epithelial wound healing.Oral Dis. 2013 Sep;19(6):551-8. doi: 10.1111/odi.12070. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Oral Dis. 2013. PMID: 23379329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mTOR signalling in corneal diseases: A recent update.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jul;213:115620. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115620. Epub 2023 May 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37217140 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on animal models of corneal epithelial-stromal injury.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Nov 18;16(11):1890-1898. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.11.23. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38028511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency: A Critical Narrative Literature Review.Ophthalmol Ther. 2024 Mar;13(3):671-696. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00880-0. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Ophthalmol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38280103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanisms related to fibroblasts in burn surface.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Aug;29(8):e13431. doi: 10.1111/srt.13431. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37632175 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in the normal and diseased cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Dec;225:109274. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109274. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 36252655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treat Corneal Injury via Autophagy Activation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 11;10:879192. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.879192. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35519619 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

