The Effects and Underlying Mechanisms of Cell Therapy on Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity After Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 32928089
- PMCID: PMC7770640
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X18666200914162013
The Effects and Underlying Mechanisms of Cell Therapy on Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity After Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
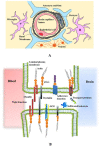
Ischemic stroke is one of the main causes of mortality and disability worldwide. However, efficient therapeutic strategies are still lacking. Stem/progenitor cell-based therapy, with its vigorous advantages, has emerged as a promising tool for the treatment of ischemic stroke. The mechanisms involve new neural cells and neuronal circuitry formation, antioxidation, inflammation alleviation, angiogenesis, and neurogenesis promotion. In the past decades, in-depth studies have suggested that cell therapy could promote vascular stabilization and decrease blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage after ischemic stroke. However, the effects and underlying mechanisms on BBB integrity induced by the engrafted cells in ischemic stroke have not been reviewed yet. Herein, we will update the progress in research on the effects of cell therapy on BBB integrity after ischemic stroke and review the underlying mechanisms. First, we will present an overview of BBB dysfunction under the ischemic condition and cells engraftment for ischemic treatment. Then, we will summarize and discuss the current knowledge about the effects and underlying mechanisms of cell therapy on BBB integrity after ischemic stroke. In particular, we will review the most recent studies in regard to the relationship between cell therapy and BBB in tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)-mediated therapy and diabetic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; blood-brain barrier; neurogenesis; stem cells; tissue plasminogen activator.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New progress in the approaches for blood-brain barrier protection in acute ischemic stroke.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Jan;144:46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30448453 Review.
-
Canonical Wnt Pathway Maintains Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity upon Ischemic Stroke and Its Activation Ameliorates Tissue Plasminogen Activator Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Sep;56(9):6521-6538. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1539-9. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30852795
-
Neural stem cell therapy for subacute and chronic ischemic stroke.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jun 13;9(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0913-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29895321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:4653936. doi: 10.1155/2017/4653936. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Stem Cells Int. 2017. PMID: 28757878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focusing on claudin-5: A promising candidate in the regulation of BBB to treat ischemic stroke.Prog Neurobiol. 2018 Feb;161:79-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Prog Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29217457 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurons Release Injured Mitochondria as "Help-Me" Signaling After Ischemic Stroke.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 3;14:785761. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.785761. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35309888 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain Barrier Dysfunction in Cerebrovascular Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(12):1166-1167. doi: 10.2174/1570159X1812201102145717. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33292116 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Emerging strategies for nerve repair and regeneration in ischemic stroke: neural stem cell therapy.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Nov 1;19(11):2430-2443. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.391313. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38526280 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Enhances the Treatment of Skin Photoaging in a Murine Model System.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025 Jan 31;18:319-330. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S490225. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39927128 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Behavioral Improvement after Combined Cell Therapy and Rehabilitation Despite Long-Term Microglia Presence in Stroke Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 3;22(4):1512. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041512. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33546370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarmah D., Kaur H., Saraf J., Pravalika K., Goswami A., Kalia K., Borah A., Wang X., Dave K.R., Yavagal D.R., Bhattacharya P. Getting closer to an effective intervention of ischemic stroke: the big promise of stem cell. Transl. Stroke Res. 2018;9(4):356–374. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0580-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zacharek A., Chen J., Cui X., Li A., Li Y., Roberts C., Feng Y., Gao Q., Chopp M. Angiopoietin1/Tie2 and VEGF/Flk1 induced by MSC treatment amplifies angiogenesis and vascular stabilization after stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(10):1684–1691. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lalu M.M., Montroy J., Dowlatshahi D., Hutton B., Juneau P., Wesch N., Zhang Y. S.; McGinn, R.; Corbett, D.; Stewart, D.J.A.; A Fergusson, D. From the lab to patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020;11(3):345–364. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00736-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

