Benchmarking hybrid assembly approaches for genomic analyses of bacterial pathogens using Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencing
- PMID: 32928108
- PMCID: PMC7490894
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-020-07041-8
Benchmarking hybrid assembly approaches for genomic analyses of bacterial pathogens using Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencing
Abstract
Background: We benchmarked the hybrid assembly approaches of MaSuRCA, SPAdes, and Unicycler for bacterial pathogens using Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencing by determining genome completeness and accuracy, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), virulence potential, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), phylogeny, and pan genome. Ten bacterial species (10 strains) were tested for simulated reads of both mediocre- and low-quality, whereas 11 bacterial species (12 strains) were tested for real reads.
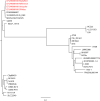
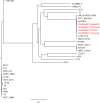
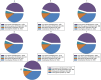
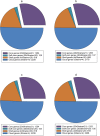
Results: Unicycler performed the best for achieving contiguous genomes, closely followed by MaSuRCA, while all SPAdes assemblies were incomplete. MaSuRCA was less tolerant of low-quality long reads than SPAdes and Unicycler. The hybrid assemblies of five antimicrobial-resistant strains with simulated reads provided consistent AMR genotypes with the reference genomes. The MaSuRCA assembly of Staphylococcus aureus with real reads contained msr(A) and tet(K), while the reference genome and SPAdes and Unicycler assemblies harbored blaZ. The AMR genotypes of the reference genomes and hybrid assemblies were consistent for the other five antimicrobial-resistant strains with real reads. The numbers of virulence genes in all hybrid assemblies were similar to those of the reference genomes, irrespective of simulated or real reads. Only one exception existed that the reference genome and hybrid assemblies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with mediocre-quality long reads carried 241 virulence genes, whereas 184 virulence genes were identified in the hybrid assemblies of low-quality long reads. The MaSuRCA assemblies of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium with mediocre-quality long reads contained 126 and 118 virulence genes, respectively, while 110 and 107 virulence genes were detected in their MaSuRCA assemblies of low-quality long reads, respectively. All approaches performed well in our MLST and phylogenetic analyses. The pan genomes of the hybrid assemblies of S. Typhimurium with mediocre-quality long reads were similar to that of the reference genome, while SPAdes and Unicycler were more tolerant of low-quality long reads than MaSuRCA for the pan-genome analysis. All approaches functioned well in the pan-genome analysis of Campylobacter jejuni with real reads.
Conclusions: Our research demonstrates the hybrid assembly pipeline of Unicycler as a superior approach for genomic analyses of bacterial pathogens using Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencing.
Keywords: Bacterial pathogen; Genomic analyses; Hybrid assembly; Illumina sequencing; MaSuRCA; Oxford Nanopore sequencing; SPAdes; Unicycler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polishing the Oxford Nanopore long-read assemblies of bacterial pathogens with Illumina short reads to improve genomic analyses.Genomics. 2021 May;113(3):1366-1377. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.03.018. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33716184
-
Benchmarking Long-Read Assemblers for Genomic Analyses of Bacterial Pathogens Using Oxford Nanopore Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 1;21(23):9161. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239161. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33271875 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analyses of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Indiana, Typhimurium, and Enteritidis isolates using MinION and MiSeq sequencing technologies.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 2;15(7):e0235641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235641. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32614888 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore sequencing technology and tools for genome assembly: computational analysis of the current state, bottlenecks and future directions.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Jul 19;20(4):1542-1559. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby017. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29617724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods for assembling complex mitochondrial genomes in land plants.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5169-5174. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae034. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38302086 Review.
Cited by
-
From Samples to Germline and Somatic Sequence Variation: A Focus on Next-Generation Sequencing in Melanoma Research.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;12(11):1939. doi: 10.3390/life12111939. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three Rounds of Read Correction Significantly Improve Eukaryotic Protein Detection in ONT Reads.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 24;12(2):247. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020247. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399651 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy and Completeness of Long Read Metagenomic Assemblies.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 30;11(1):96. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010096. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677391 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing-Based Resistome Analysis of Nosocomial Multidrug-Resistant Non-Fermenting Gram-Negative Pathogens from the Balkans.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 3;11(3):651. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030651. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Genetically Modified Microorganisms Using Short- and Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Contaminations of Related Origin in Multiple Commercial Food Enzyme Products.Foods. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2637. doi: 10.3390/foods10112637. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34828918 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

