The relations among worry, meta-worry, intolerance of uncertainty and attentional bias for threat in men at high risk for generalized anxiety disorder: a network analysis
- PMID: 32928164
- PMCID: PMC7491186
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-020-02849-w
The relations among worry, meta-worry, intolerance of uncertainty and attentional bias for threat in men at high risk for generalized anxiety disorder: a network analysis
Abstract
Background: Improving the psychotherapies for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is dependent on a deeper understanding of the relations between GAD and its associated cognitive factors. In the present study, we investigate how the core feature of GAD (i.e., worry) and its associated cognitive factors, such as meta-worry, intolerance of uncertainty, and attention bias towards threat, relate to each other in men at high risk for GAD.
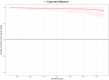
Methods: We used network analysis to explore the relations among these variables in a cross-sectional sample of 122 men at high risk for generalized anxiety disorder. Specifically, we computed the expected influence and predictability of each variable.
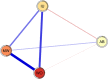
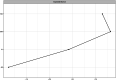
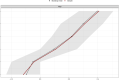
Results: In the final network, we found that worry and meta-worry had the highest expected influence and predictability. In contrast, attention bias towards threat showed the lowest expected influence and predictability. The estimates of the expected influence of the nodes were stable (correlation stability coefficient = 0.52).
Conclusions: The present study is the first to investigate the relations among worry, meta-worry, intolerance of uncertainty, and attention bias towards threat in men at high risk for generalized anxiety disorder. These findings indicate that worry and meta-worry may play important roles in the present network. The implications for clinical interventions and future studies are discussed.
Keywords: Attention bias; Generalized anxiety disorder; High risk; Intolerance of uncertainty; Meta-worry; Network analysis; Worry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relations between different components of intolerance of uncertainty and symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a network analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 10;21(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03455-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34507563 Free PMC article.
-
What's in a name? Intolerance of uncertainty, other uncertainty-relevant constructs, and their differential relations to worry and generalized anxiety disorder.Cogn Behav Ther. 2017 Mar;46(2):141-161. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2016.1211172. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Cogn Behav Ther. 2017. PMID: 27684470
-
The effect of uncertainty on attentional bias in subclinical worriers: Evidence from reaction time and eye-tracking.J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2023 Dec;81:101842. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2023.101842. Epub 2023 Feb 16. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36827945 Clinical Trial.
-
Current theoretical models of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): conceptual review and treatment implications.J Anxiety Disord. 2009 Dec;23(8):1011-23. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.07.006. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Anxiety Disord. 2009. PMID: 19700258 Review.
-
[Etiological factors of generalized anxiety disorder].Encephale. 2003 Jul-Aug;29(4 Pt 1):351-61. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14615705 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Executive Functioning Constructs in Anxiety, Obsessive-Compulsive, Post-Traumatic Stress, and Related Disorders.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022 Dec;24(12):871-880. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01390-9. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022. PMID: 36401677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment condition as a moderator and change in trait mindfulness as a mediator of a brief mindfulness ecological momentary intervention for generalized anxiety disorder.Eur Psychiatry. 2024 May 7;67(1):e40. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.1750. Eur Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38711385 Free PMC article.
-
Online versus face-to-face metacognitive educational counseling program on anxiety and meta-worry in women with a history of miscarriage: A randomized clinical trial.J Educ Health Promot. 2022 Aug 25;11:264. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1292_21. eCollection 2022. J Educ Health Promot. 2022. PMID: 36325205 Free PMC article.
-
Mental Health Concerns in Patients with COVID-19: A Network Analysis.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2025 May 17;18:1125-1137. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S524256. eCollection 2025. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2025. PMID: 40406339 Free PMC article.
-
Verbal Weight-Related Abuse and Binge Eating Behavior: The Mediating Role of Attentional Bias to Threat Cues and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation.Brain Behav. 2024 Oct;14(10):e70054. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70054. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39344340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Tyrer P, Baldwin D. Generalised anxiety disorder. Lancet. 2006;368(9553):2156–2166. - PubMed
-
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Monahan PO, Lowe B. Anxiety disorders in primary care: prevalence, impairment, comorbidity, and detection. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146(5):317–325. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, DuPont RL, Berglund P, Wittchen HU. Impairment in pure and comorbid generalized anxiety disorder and major depression at 12 months in two national surveys. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156(12):1915–1923. - PubMed
-
- Yonkers KA, Warshaw MG, Massion AO, Keller MB. Phenomenology and course of generalised anxiety disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 1996;168(3):308–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

