Yan-Hou-Qing formula attenuates ammonia-induced acute pharyngitis in rats via inhibition of NF-κB and COX-2
- PMID: 32928206
- PMCID: PMC7491126
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-020-03077-1
Yan-Hou-Qing formula attenuates ammonia-induced acute pharyngitis in rats via inhibition of NF-κB and COX-2
Abstract
Background: Yan Hou Qing (YHQ) is a Chinese medicinal formula designed to alleviate sore throat symptoms, but underlying mechanism of YHQ treatment for pharyngitis is poorly defined up to now.
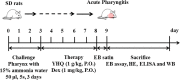
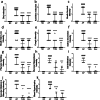
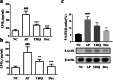
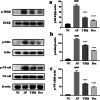
Methods: In this study, the modulation of YHQ on pharyngitis is investigated in ammonia-induced acute pharyngitis rat models. After treatment with YHQ or dexamethasone respectively for five consecutive days, all rats were sacrificed for biomolecular and histopathologic study. Protein expressions of MAPKs, NF-κB, COX-2 and 5-LOX in pharyngitis tissue were evaluated by western blot analysis and the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, prostaglandin (PG) E2, leukotrienes (LT)-B4 and LT-D4 in pharyngeal tissue were measured via ELISA assay. Evans blue (EB) dye exudation test was performed parallelly to assess the integrity of pharyngeal tissue.
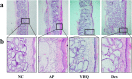
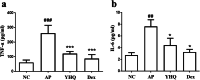
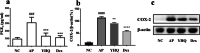
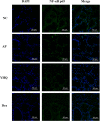
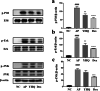
Results: Compared with normal control group, EB dye exudation, and inflammatory cytokines in the model group were significantly increased, and the pharynx tissue was obviously infiltrated by inflammatory cells. YHQ treatment improved the inflammatory infiltrate in pharyngeal tissue, and reduced EB dye exudation in AP rat models. The up-regulated TNF-α and IL-6 in pharyngeal tissue of AP were significantly reduced by YHQ through inhibition of phosphorylation of p38, Erk and NF-κB. YHQ treatment also reversed the increased level of PGE2 through down-regulation of COX-2.
Conclusions: YHQ formula attenuated the pharyngitis related symptoms via suppression of COX-2 and phosphorylation of p38, Erk and NF-κB (p65).
Keywords: Inflammation; NF-κB; COX-2; Pharyngitis; Yan Hou Qing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yan-Hou-Qing formula attenuates allergic airway inflammation via up-regulation of Treg and suppressing Th2 responses in Ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 1;231:275-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.038. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30496840
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Ganluyin, a Chinese classic prescription, in chronic pharyngitis rat model.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Aug 28;20(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03057-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32859182 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides, the active component of Dendrobiumofficinale flower, ameliorates chronic pharyngitis in rats via TLR4/NF-κb pathway regulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118620. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118620. Epub 2024 Jul 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39067830
-
Therapeutic effect of Hosta plantaginea (Lam.) Aschers flowers on acute pharyngitis through inhibition of multi-inflammatory pathways in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116966. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116966. Epub 2023 Jul 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37499845
-
[Effects of different extracts of Dendrobium officinale on rats with chronic pharyngitis induced by pepper water combined with ammonia].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 May;47(9):2525-2532. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211223.703. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35531700 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Antipharyngitis Effects of Syringa oblata L. Ethanolic Extract in Acute Pharyngitis Rat Model and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ir-Idoids in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 10;2021:5111752. doi: 10.1155/2021/5111752. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34925529 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Action Mechanism and Validation of the Key Pathways of Dendrobium officinale Throat-clearing Formula for the Treatment of Chronic Pharyngitis Based on Network Pharmacology.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(3):479-496. doi: 10.2174/0113862073261351231005111817. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37877149 Free PMC article.
-
Tinosporae Radix attenuates acute pharyngitis by regulating glycerophospholipid metabolism and inflammatory responses through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 6;15:1491321. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1491321. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39568590 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

