Newborn's first bath: any preferred timing? A pilot study from Lebanon
- PMID: 32928289
- PMCID: PMC7491191
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-020-05282-0
Newborn's first bath: any preferred timing? A pilot study from Lebanon
Abstract
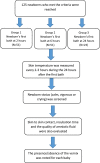
Objective: To try to find the most appropriate time for the newborn's first bath. This prospective randomized study was conducted in one hospital (July-September 2017).
Results: A higher percentage of newborns who had a skin-to-skin contact with their mothers had their bath at 24 h vs 2 h after birth (65.2% vs 33.3%; p = 0.01). A higher percentage of mothers who helped in their baby's bath had their baby's bath at 24 h vs 2 h (65.2% vs 5.9%; p < 0.001) and vs 6 h (65.2% vs 15.7%; p < 0.001) respectively. A higher mean incubation time was seen between newborns who had their bath at 2 h (2.10 vs 1.78; p = 0.002) and 6 h (2.18 vs 1.78; p = 0.003) compared to those who had their bath at 24 h respectively. A higher percentage of newborns who took their first bath 24 h after birth were calm compared to crying vigorously (38.6% vs 9.1%; p = 0.04). Delaying newborn first bath until 24 h of life was associated with benefits (reducing hypothermia and vigorous crying, benefit from the vernix caseosa on the skin and adequate time of skin-to-skin contact and mother participation in her child's bathing.
Keywords: 24-h status; Bathing time; Incubation time; Neonates; Vernix caseosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kuller JM. Update on newborn bathing. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev. 2014;14(4):166–170. doi: 10.1053/j.nainr.2014.10.006. - DOI
-
- WHO recommendations on postnatal care of the mother and newborn. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/97603/9789241506649_eng... - PubMed
-
- New K. Evidence-based guidelines for infant bathing. 2019. https://www.researchreview.co.nz/getmedia/0a9e5190-b8ac-419f-8f44-43b8e5...
-
- Clinical Guidelines And Evidence Review For Post Natal Care: Routine Post Natal Care Of Recently Delivered Women And Their Babies. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg37/evidence/full-guideline-485782237
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical