Motivational processes in physical education and objectively measured physical activity among adolescents
- PMID: 32928449
- PMCID: PMC7498624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2019.06.001
Motivational processes in physical education and objectively measured physical activity among adolescents
Abstract
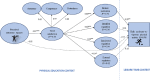
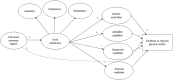
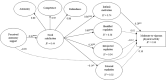
Purpose: Grounded in self-determination theory (SDT), the present study tested how students' perceptions of autonomy support from physical education teachers predicts objectively measured moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) of adolescents. According to SDT, it was expected that psychological needs and autonomous and controlled forms of motivation would mediate these relationships.
Methods: Students (n = 397) aged from 11 to 15 years in 17 different schools filled in questionnaires regarding SDT variables. In addition, objective MVPA was measured using an accelerometer (ActiGraph GT3X; ActiGraph, Pensacola, FL, USA) for 7 days. Structural equation modelling was used to examine the hypothesized relationships among the study variables.
Results: The theory-based model showed a good fit with the data: χ2 = 642.464, df = 257; comparative fit index = 0.932; non-normed fit index = 0.921; root mean square error of approximation = 0.062; root mean square error of approximation 90% confidence interval: 0.054-0.067. As hypothesized, there was a significant and positive direct relationship between autonomy support and need satisfaction (β = 0.81, p = 0.001). In turn, need satisfaction positively predicted intrinsic motivation (β = 0.86, p = 0.001). Intrinsic motivation was positively related to MVPA (β = 0.29, p = 0.009). A significant indirect effect (β = 0.20, p = 0.004) supported the mediating role of psychological need satisfaction and intrinsic motivation in the relationship between perceived autonomy support and objectively measured MVPA.
Conclusion: The findings of the current study support the applicability of the SDT-based model in explaining the antecedents of objectively measured MVPA of adolescents. To enhance adolescents' daily MVPA, special focus should be put on increasing their intrinsic motivation toward physical education.
Keywords: Accelerometer; Motivation; Physical activity; Physical education; Self-determination theory.
Copyright © 2019. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using the self-determination theory to understand Chinese adolescent leisure-time physical activity.Eur J Sport Sci. 2017 May;17(4):453-461. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2016.1276968. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Eur J Sport Sci. 2017. PMID: 28100122
-
Perceived Controlling Behaviors of Physical Education Teachers and Objectively Measured Leisure-Time Physical Activity in Adolescents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jul 30;16(15):2709. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152709. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31366009 Free PMC article.
-
Web-based intervention program to foster need-supportive behaviors in physical education teachers and parents: a cluster-randomized controlled study to increase students' intention and effort to engage in physical activity.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jun 10;25(1):2142. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22590-x. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40495137 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Motivating children with developmental coordination disorder in school physical education: the self-determination theory approach.Res Dev Disabil. 2011 Nov-Dec;32(6):2674-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2011.06.005. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Res Dev Disabil. 2011. PMID: 21742467 Review.
-
Does Self-Determination Theory Associate With Physical Activity? A Systematic Review of Systematic Review.Int J Psychol. 2025 Jun;60(3):e70044. doi: 10.1002/ijop.70044. Int J Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40256835 Review.
Cited by
-
Web-based need-supportive parenting program to promote physical activity in secondary school students: a randomized controlled pilot trial.BMC Public Health. 2023 Aug 25;23(1):1627. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16528-4. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37626288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Academic motivation in adolescents: the role of parental autonomy support, psychological needs satisfaction and self-control.Front Psychol. 2024 May 10;15:1384695. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1384695. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38800688 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Exergames on Physical Fitness, Body Composition and Enjoyment in Children: A Six-Month Intervention Study.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;11(10):1172. doi: 10.3390/children11101172. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457137 Free PMC article.
-
Determinant Factors of Achievement Motivation in School Physical Education.Children (Basel). 2022 Sep 8;9(9):1366. doi: 10.3390/children9091366. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138675 Free PMC article.
-
Changing trajectory of daily physical activity levels among at-risk adolescents: influences of motivational mechanisms.BMC Public Health. 2023 Oct 25;23(1):2089. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16949-1. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37880639 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Grgic J., Dumuid D., Bengoechea E.G., Shrestha N., Bauman A., Olds T. Health outcomes associated with reallocations of time between sleep, sedentary behavior, and physical activity: a systematic scoping review of isotemporal substitution studies. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2018;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s12966-018-0691-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evenson K.R., Catellier D.J., Gill K., Ondrak K.S., McMurray R.G. Calibration of two objective measures of physical activity for children. J Sport Sci. 2008;26:1557–1565. - PubMed
-
- Van Hecke L., Loyen A., Verloigne M., Ploeg H.P., Lakerveld J., Brug J. Variation in population levels of physical activity in European children and adolescents according to cross-European studies: a systematic literature review within DEDIPAC. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2016;13:70. doi: 10.1186/s12966-016-0396-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

