Child with tuberculous meningitis and COVID-19 coinfection complicated by extensive cerebral sinus venous thrombosis
- PMID: 32928816
- PMCID: PMC7490923
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238597
Child with tuberculous meningitis and COVID-19 coinfection complicated by extensive cerebral sinus venous thrombosis
Abstract
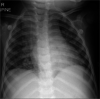
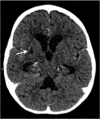
We herein report a case of a child with tuberculous meningitis and COVID-19 coinfection complicated by hydrocephalus, arterial ischaemic stroke and extensive cerebral sinus venous thrombosis. Both conditions induce a proinflammatory cytokine drive resulting, among others, in a prothrombotic state. The disruption of the coagulation system in this case was supported by elevated D-dimers, fibrinogen and ferritin levels, consistent with thrombotic complications reported in some adult patients infected with COVID-19. The child also exhibited prolonged viral shedding that suggests severe disease.
Keywords: global health; infections; neurology (drugs and medicines); paediatrics (drugs and medicines); radiology (diagnostics).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- COVID-19 in the who African region. Available: https://who.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/0c9b3a8b68d043...
-
- World Health Organization Global tuberculosis report. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Report, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
