Evaluation of a program using a physician assistant and an electronic patient-provider communication tool to facilitate discussions about goals of care in older adults in hospital: a pilot study
- PMID: 32928879
- PMCID: PMC7505521
- DOI: 10.9778/cmajo.20200022
Evaluation of a program using a physician assistant and an electronic patient-provider communication tool to facilitate discussions about goals of care in older adults in hospital: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Many patients receive unwanted, low-value, high-intensity care at the end of life because of poor communication with health care providers. Our aim was to evaluate the feasibility of using a physician assistant and an electronic tool to facilitate discussions about goals of care.
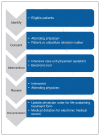
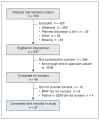
Method: We conducted a pilot study for the intervention (physician assistant-led discussion using an electronic tool) from Apr. 1 to Aug. 31, 2019. Patients aged 79 years or older admitted to the Royal Victoria Hospital (Barrie, Ontario) with either (i) no documented resuscitation preferences or (ii) a request for life-sustaining treatments in the event of a life-threatening illness were eligible for the intervention. The goal of this study was to complete more than 30 interventions. The primary outcomes included the proportion of consenting eligible patients, the time required and the proportion of patients changing their resuscitation preferences.
Results: A total of 763 patients met the inclusion criteria, with 337 eligible for the intervention. Of these, 49 cases were contacted for consent, and 37 interventions were completed (75.5%, 95% confidence interval [CI] 61.1%-86.6%). On average, the intervention required 50 minutes (standard deviation 21) to complete. Overall, 31 interventions resulted in a change in resuscitation preferences (83.7%, 95% CI 68.0%-93.8%), with 22 patients choosing to forgo any access to life-sustaining treatments in the event of a life-threatening illness (59.4%, 95% CI 42.1%-75.2%).
Interpretation: In this pilot study, the intervention was completed in a minority of eligible patients and required substantial time; however, it led to many changes in resuscitation preferences. Before designing a study to evaluate its impact, the intervention needs to be revised to make it more efficient to administer.
Copyright 2020, Joule Inc. or its licensors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advance directives for seriously ill hospitalized patients: effectiveness with the patient self-determination act and the SUPPORT intervention. SUPPORT Investigators. Study to Understand Prognoses and Preferences for Outcomes and Risks of Treatment.J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997 Apr;45(4):500-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1997.tb05178.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997. PMID: 9100721 Clinical Trial.
-
Patient preferences for communication with physicians about end-of-life decisions. SUPPORT Investigators. Study to Understand Prognoses and Preference for Outcomes and Risks of Treatment.Ann Intern Med. 1997 Jul 1;127(1):1-12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-1-199707010-00001. Ann Intern Med. 1997. PMID: 9214246 Clinical Trial.
-
A controlled trial to improve care for seriously ill hospitalized patients. The study to understand prognoses and preferences for outcomes and risks of treatments (SUPPORT). The SUPPORT Principal Investigators.JAMA. 1995 Nov 22-29;274(20):1591-8. JAMA. 1995. PMID: 7474243 Clinical Trial.
-
Communication about serious illness care goals: a review and synthesis of best practices.JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Dec;174(12):1994-2003. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.5271. JAMA Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 25330167 Review.
-
Communication in palliative care: talking about the end of life, before the end of life.Postgrad Med J. 2016 Aug;92(1090):466-70. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2015-133368. Epub 2016 May 6. Postgrad Med J. 2016. PMID: 27153866 Review.
References
-
- Simon JE, Ghosh S, Heyland D, et al. Evidence of increasing public participation in advance care planning: a comparison of polls in Alberta between 2007 and 2013. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2019;9:189–96. - PubMed
-
- Wendler D, Rid A. Systematic review: the effect on surrogates of making treatment decisions for others. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154:336–46. - PubMed
-
- Bekelman JE, Halpern SD, Blankart CR, et al. Comparison of site of death, health care utilization, and hospital expenditures for patients dying with cancer in 7 developed countries. JAMA. 2016;315:272–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
