A new malaria vector in Africa: Predicting the expansion range of Anopheles stephensi and identifying the urban populations at risk
- PMID: 32929020
- PMCID: PMC7547157
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2003976117
A new malaria vector in Africa: Predicting the expansion range of Anopheles stephensi and identifying the urban populations at risk
Abstract
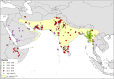
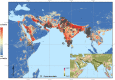
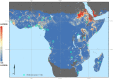
In 2012, an unusual outbreak of urban malaria was reported from Djibouti City in the Horn of Africa and increasingly severe outbreaks have been reported annually ever since. Subsequent investigations discovered the presence of an Asian mosquito species; Anopheles stephensi, a species known to thrive in urban environments. Since that first report, An. stephensi has been identified in Ethiopia and Sudan, and this worrying development has prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to publish a vector alert calling for active mosquito surveillance in the region. Using an up-to-date database of published locational records for An. stephensi across its full range (Asia, Arabian Peninsula, Horn of Africa) and a set of spatial models that identify the environmental conditions that characterize a species' preferred habitat, we provide evidence-based maps predicting the possible locations across Africa where An. stephensi could establish if allowed to spread unchecked. Unsurprisingly, due to this species' close association with man-made habitats, our maps predict a high probability of presence within many urban cities across Africa where our estimates suggest that over 126 million people reside. Our results strongly support the WHO's call for surveillance and targeted vector control and provide a basis for the prioritization of surveillance.
Keywords: ensemble modeling; invasive species; species distribution model; urban malaria; vector.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization , World Malaria Report, (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2018), p. 210.
-
- Coetzee M., Distribution of the African malaria vectors of the Anopheles gambiae complex. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 70, 103–104 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Coluzzi M., The clay feet of the malaria giant and its African roots: Hypotheses and inferences about origin, spread and control of Plasmodium falciparum. Parassitologia 41, 277–283 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Gillies M. T., de Meillon B., The Anophelinae of Africa South of the Sahara (Ethiopian Zoogeographical Region), (The South African Institute for Medical Research, Johannesburg, ed. 2, 1968).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

