Victorin, the host-selective cyclic peptide toxin from the oat pathogen Cochliobolus victoriae, is ribosomally encoded
- PMID: 32929037
- PMCID: PMC7533671
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2010573117
Victorin, the host-selective cyclic peptide toxin from the oat pathogen Cochliobolus victoriae, is ribosomally encoded
Erratum in
-
Correction for Kessler et al., Victorin, the host-selective cyclic peptide toxin from the oat pathogen Cochliobolus victoriae, is ribosomally encoded.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 8;117(49):31548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2022479117. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33199652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
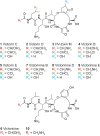
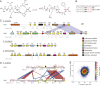
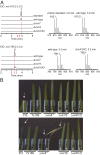
The necrotrophic fungal pathogen Cochliobolus victoriae produces victorin, a host-selective toxin (HST) essential for pathogenicity to certain oat cultivars with resistance against crown rust. Victorin is a mixture of highly modified heterodetic cyclic hexapeptides, previously assumed to be synthesized by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Herein, we demonstrate that victorin is a member of the ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptide (RiPP) family of natural products. Analysis of a newly generated long-read assembly of the C. victoriae genome revealed three copies of precursor peptide genes (vicA1-3) with variable numbers of "GLKLAF" core peptide repeats corresponding to the victorin peptide backbone. vicA1-3 are located in repeat-rich gene-sparse regions of the genome and are loosely clustered with putative victorin biosynthetic genes, which are supported by the discovery of compact gene clusters harboring corresponding homologs in two distantly related plant-associated Sordariomycete fungi. Deletion of at least one copy of vicA resulted in strongly diminished victorin production. Deletion of a gene encoding a DUF3328 protein (VicYb) abolished the production altogether, supporting its predicted role in oxidative cyclization of the core peptide. In addition, we uncovered a copper amine oxidase (CAO) encoded by vicK, in which its deletion led to the accumulation of new glycine-containing victorin derivatives. The role of VicK in oxidative deamination of the N-terminal glycyl moiety of the hexapeptides to the active glyoxylate forms was confirmed in vitro. This study finally unraveled the genetic and molecular bases for biosynthesis of one of the first discovered HSTs and expanded our understanding of underexplored fungal RiPPs.
Keywords: Cochliobolus; RiPP; copper amine oxidase; host-selective toxin; victorin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of victorin sensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):577-82. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.577. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195940
-
Characterization of the LOV1-mediated, victorin-induced, cell-death response with virus-induced gene silencing.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Aug;26(8):903-17. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-01-13-0014-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 23634836
-
Virulence, Host-Selective Toxin Production, and Development of Three Cochliobolus Phytopathogens Lacking the Sfp-Type 4'-Phosphopantetheinyl Transferase Ppt1.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015 Oct;28(10):1130-41. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-15-0068-R. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015. PMID: 26168137
-
Genetic and genomic dissection of the Cochliobolus heterostrophus Tox1 locus controlling biosynthesis of the polyketide virulence factor T-toxin.Adv Genet. 2007;57:219-61. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2660(06)57006-3. Adv Genet. 2007. PMID: 17352906 Review.
-
Discovery of novel fungal RiPP biosynthetic pathways and their application for the development of peptide therapeutics.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jul;103(14):5567-5581. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09893-x. Epub 2019 May 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31147756 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Functional Analysis of Peptides Derived from KEX2-Processed Repeat Proteins in Agaricomycetes Using Reverse Genetics and Peptidomics.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0202122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02021-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36314921 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfide bridge-targeted metabolome mining unravels an antiparkinsonian peptide.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Feb;14(2):881-892. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.09.006. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38322339 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatic side-chain crosslinking in RiPP biosynthesis.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Feb;21(2):168-181. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01795-y. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39814993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Venturia inaequalis effector repertoire is dominated by expanded families with predicted structural similarity, but unrelated sequence, to avirulence proteins from other plant-pathogenic fungi.BMC Biol. 2022 Nov 3;20(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01442-9. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 36329441 Free PMC article.
-
cblaster: a remote search tool for rapid identification and visualization of homologous gene clusters.Bioinform Adv. 2021 Aug 5;1(1):vbab016. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbab016. eCollection 2021. Bioinform Adv. 2021. PMID: 36700093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meehan F., Murphy H. C., A new Helminthosporium blight of oats. Science 104, 413–414 (1946). - PubMed
-
- Meehan F., Murphy H. C., Differential phytotoxicity of metabolic by-products of Helminthosporium victoriae. Science 106, 270–271 (1947). - PubMed
-
- Wolpert T. J., Dunkle L. D., Ciuffetti L. M., Host-selective toxins and avirulence determinants: What’s in a name? Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 40, 251–285 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Petrov V., Qureshi M. K., Hille J., Gechev T., Occurrence, biochemistry and biological effects of host-selective plant mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 112, 251–264 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Wolpert T. J., Lorang J. M., Victoria Blight, defense turned upside down. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 95, 8–13 (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

