Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases
- PMID: 32929074
- PMCID: PMC7490424
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00303-7
Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases
Abstract
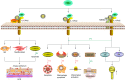
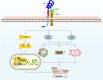
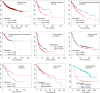
Non-enzymatic chitinase-3 like-protein-1 (CHI3L1) belongs to glycoside hydrolase family 18. It binds to chitin, heparin, and hyaluronic acid, and is regulated by extracellular matrix changes, cytokines, growth factors, drugs, and stress. CHI3L1 is synthesized and secreted by a multitude of cells including macrophages, neutrophils, synoviocytes, chondrocytes, fibroblast-like cells, smooth muscle cells, and tumor cells. It plays a major role in tissue injury, inflammation, tissue repair, and remodeling responses. CHI3L1 has been strongly associated with diseases including asthma, arthritis, sepsis, diabetes, liver fibrosis, and coronary artery disease. Moreover, following its initial identification in the culture supernatant of the MG63 osteosarcoma cell line, CHI3L1 has been shown to be overexpressed in a wealth of both human cancers and animal tumor models. To date, interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2, transmembrane protein 219, galectin-3, chemo-attractant receptor-homologous 2, and CD44 have been identified as CHI3L1 receptors. CHI3L1 signaling plays a critical role in cancer cell growth, proliferation, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, activation of tumor-associated macrophages, and Th2 polarization of CD4+ T cells. Interestingly, CHI3L1-based targeted therapy has been increasingly applied to the treatment of tumors including glioma and colon cancer as well as rheumatoid arthritis. This review summarizes the potential roles and mechanisms of CHI3L1 in oncogenesis and disease pathogenesis, then posits investigational strategies for targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Johansen JS, Williamson MK, Rice JS, Price PA. Identification of proteins secreted by human osteoblastic cells in culture. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1992;7:501–512. - PubMed
-
- Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD. Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:25803–25810. - PubMed
-
- Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ. Identification of a 38-kDa heparin-binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:13076–13083. - PubMed
-
- Junker N, Johansen JS, Andersen CB, Kristjansen PE. Expression of YKL-40 by peritumoral macrophages in human small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2005;48:223–231. - PubMed
-
- Recklies AD, White C, Ling H. The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC-gp39) stimulates proliferation of human connective-tissue cells and activates both extracellular signal-regulated kinase- and protein kinase B-mediated signalling pathways. Biochem. J. 2002;365:119–126. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

