Dense neuronal reconstruction through X-ray holographic nano-tomography
- PMID: 32929244
- PMCID: PMC8354006
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-020-0704-9
Dense neuronal reconstruction through X-ray holographic nano-tomography
Abstract
Imaging neuronal networks provides a foundation for understanding the nervous system, but resolving dense nanometer-scale structures over large volumes remains challenging for light microscopy (LM) and electron microscopy (EM). Here we show that X-ray holographic nano-tomography (XNH) can image millimeter-scale volumes with sub-100-nm resolution, enabling reconstruction of dense wiring in Drosophila melanogaster and mouse nervous tissue. We performed correlative XNH and EM to reconstruct hundreds of cortical pyramidal cells and show that more superficial cells receive stronger synaptic inhibition on their apical dendrites. By combining multiple XNH scans, we imaged an adult Drosophila leg with sufficient resolution to comprehensively catalog mechanosensory neurons and trace individual motor axons from muscles to the central nervous system. To accelerate neuronal reconstructions, we trained a convolutional neural network to automatically segment neurons from XNH volumes. Thus, XNH bridges a key gap between LM and EM, providing a new avenue for neural circuit discovery.
Figures
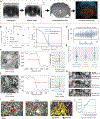
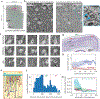

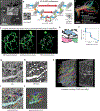

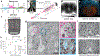

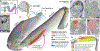
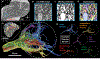
Comment in
-
X-ray connectomics.Nat Methods. 2020 Nov;17(11):1072. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-00994-4. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 33122856 No abstract available.
References
Methods References
Extended Data References
-
- . Hodgkin HM & Bryant PJ Scanning electron microscopy of the adult of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Biol. Drosoph. (1979).
-
- . Court RC et al. A Systematic Nomenclature for the Drosophila Ventral Nervous System. bioRxiv 122952 (2017) doi:10.1101/122952. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

