Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy
- PMID: 32929287
- PMCID: PMC8517961
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-0684-4
Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy.Nat Genet. 2020 Nov;52(11):1266. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-00718-6. Nat Genet. 2020. PMID: 32948852
Abstract
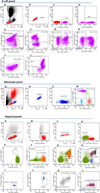
We report on the influence of ~22 million variants on 731 immune cell traits in a cohort of 3,757 Sardinians. We detected 122 significant (P < 1.28 × 10-11) independent association signals for 459 cell traits at 70 loci (53 of them novel) identifying several molecules and mechanisms involved in cell regulation. Furthermore, 53 signals at 36 loci overlapped with previously reported disease-associated signals, predominantly for autoimmune disorders, highlighting intermediate phenotypes in pathogenesis. Collectively, our findings illustrate complex genetic regulation of immune cells with highly selective effects on autoimmune disease risk at the cell-subtype level. These results identify drug-targetable pathways informing the design of more specific treatments for autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


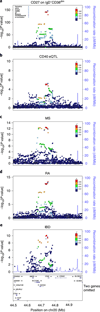
Comment in
-
Unravelling the complex genetic regulation of immune cells.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Mar;17(3):131-132. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00563-1. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33328616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patin E et al. Natural variation in the parameters of innate immune cells is preferentially driven by genetic factors. Nat. Immunol. 19, 302–314 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

