What are the drugs having potential against COVID-19?
- PMID: 32929317
- PMCID: PMC7481551
- DOI: 10.1007/s00044-020-02625-1
What are the drugs having potential against COVID-19?
Abstract
A disease emerged in the city of Wuhan, Hubei Province, Central China in the last month of 2019. It was pneumonia caused by a newly emerged coronavirus called COVID-19, later. Coronaviruses are enveloped RNA viruses belong to the Betacoronavirus family and infected birds, humans, and other mammals. In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared the COVID-19 outbreak could be characterized as a global pandemic because the disease spread, and a large number of people were infected and died in many countries on different continents by virtue of this new virus. Now, intensive work is underway about the pathogenic mechanisms and epidemiological properties of COVID-19, and a great effort is made to develop effective specific therapeutic drugs, vaccines, and/or treatment strategies against these diseases. Herein, we have focused on all treatment options available against COVID-19 pneumonia in this text.
Keywords: Antiviral; COVID-19; Cellular therapy; Drug; Immunotherapy; Pandemic.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

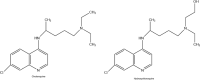
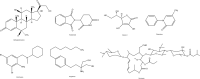
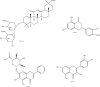
References
-
- Agostini ML, Andres EL, Sims AC, Graham RL, Sheahan TP, Lu X, Smith EC, Case JB, Feng JY, Jordan R, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Siegel D, Mackman RL, Clarke MO, Baric RS, Denison MR. Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. mBio. 2018;9:e00221–e002218. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anti-2019-nCoV Volunteers, Li Z, Wu M, Yao J, Guo J, Liao X, Song S, Li J, Duan G, Zhou Y, Wu X, Zhou Z, Wang T, Hu M, Chen X, Fu Y, Lei C, Dong H, Xu C, Hu Y, Han M, Zhou Y, Jia H, Chen X, Yan J (2020) Caution on kidney dysfunctions of COVID-19 patients. medRxiv. 10.1101/2020.02.08.20021212
-
- Arabi Y, Balkhy H, Hajeer AH, Bouchama A, Hayden FG, Al-Omari A, Al-Hameed FM, Taha Y, Shindo N, Whitehead J, Merson L, AlJohani S, Al-Khairy K, Carson G, Luke TC, Hensley L, Al-Dawood A, Al-Qahtani S, Modjarrad K, Sadat M, Rohde G, Leport C, Fowler R. Feasibility, safety, clinical, and laboratory effects of convalescent plasma therapy for patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a study protocol. Springerplus. 2015;4:709. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arabi YM, Alothman A, Balkhy HH, Al-Dawood A, AlJohani S, Al Harbi S, Kojan S, Al Jeraisy M, Deeb AM, Assiri AM, Al-Hameed F, AlSaedi A, Mandourah Y, Almekhlafi GA, Sherbeeni NM, Elzein FE, Memon J, Taha Y, Almotairi A, Maghrabi KA, Qushmaq I, Al Bshabshe A, Kharaba A, Shalhoub S, Jose J, Fowler RA, Hayden FG, Hussein MA, The MIRACLE trial group Treatment of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome with a combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2018;19:81. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
