Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via AMPK-FOXO1-ULK1 signaling axis-mediated autophagy
- PMID: 32929346
- PMCID: PMC7481427
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.47045
Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via AMPK-FOXO1-ULK1 signaling axis-mediated autophagy
Abstract
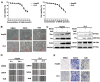
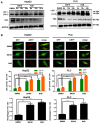
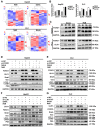
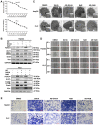
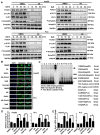
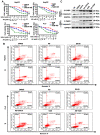
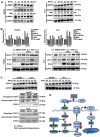
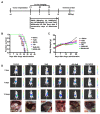
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most frequent cause of cancer-related deaths globally because of high metastasis and recurrence rates. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of HCC recurrence and metastasis and developing effective targeted therapies are expected to improve patient survival. The promising anti-cancer agents for the treatment of hematological malignancies, histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDIs), have limited effects against epithelial cell-derived cancers, including HCC, the mechanisms involved have not been elucidated. Herein, we studied the molecular mechanisms underlying HDI-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) involving FOXO1-mediated autophagy. Methods: The biological functions of HDIs in combination with autophagy inhibitors were examined both in vitro and in vivo. Cell autophagy was assessed using the generation of mRFP-GFP-LC3-expressing cells and fluorescent LC3 puncta analysis, Western blotting, and electron microscopy. An orthotopic hepatoma model was established in mice for the in vivo experiments. Results: Our study provided novel mechanistic insights into HDI-induced EMT mediated by the autophagy AMPK-FOXO1-ULK1-Snail signaling axis. We demonstrated that autophagy served as a pro-metastasis mechanism in HDI-treated hepatoma cells. HDIs induced autophagy via a FOXO1-dependent pathway, and FOXO1 inhibition promoted HDI-mediated apoptosis in hepatoma cells. Thus, our findings provided novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying HDI-induced EMT involving FOXO1-mediated autophagy and demonstrated that a FOXO1 inhibitor exerted a synergistic effect with an HDI to inhibit cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Conclusion: We demonstrated that HDIs triggers FOXO1-dependent autophagy, which ultimately promotes EMT, limiting the clinical outcome of HDI-based therapies. Our study suggests that the combination of an HDI and a FOXO1 inhibitor is an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: Autophagy; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FOXO1 inhibitor; Histone deacetylase inhibitors; Metastasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formosanin C induces autophagy-mediated cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma through activating DUSP1/AMPK/ULK1/Beclin1 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Mar;138:156404. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156404. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39862789
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate Snail via Smad2/3 phosphorylation and stabilization of Snail to promote metastasis of hepatoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2018 Apr 28;420:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.068. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29410023
-
FOXO1 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by reversing ZEB2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):1703-1713. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13786. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27924058 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing function of EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma: From biological view to nanotechnological standpoint.Environ Res. 2023 Jun 15;227:115683. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115683. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36933639 Review.
-
Wnt Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cells. 2024 Dec 2;13(23):1990. doi: 10.3390/cells13231990. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Purple sweet potato delphinidin-3-rutin represses glioma proliferation by inducing miR-20b-5p/Atg7-dependent cytostatic autophagy.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022 Jul 31;26:314-329. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.07.007. eCollection 2022 Sep 15. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022. PMID: 36090477 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the hsa_circ_0039466/miR-96-5p/FOXO1 regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma by whole-transcriptome analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(14):769. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3147. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35965793 Free PMC article.
-
H3K36me2 methyltransferase NSD2/WHSC1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer metastasis via activation of ULK1-dependent autophagy.Autophagy. 2025 Aug;21(8):1824-1842. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2025.2479995. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Autophagy. 2025. PMID: 40097917 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian hormones-autophagy-immunity axis in menstruation and endometriosis.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3512-3526. doi: 10.7150/thno.55241. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methyl Gallate Suppresses the Migration, Invasion, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via the AMPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in vitro and in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 13;13:894285. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.894285. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35770085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M. et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D, Finn RS. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:599–616. - PubMed
-
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:769–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

