Alzheimer's disease: natural products as inhibitors of neuroinflammation
- PMID: 32930914
- PMCID: PMC7572326
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-020-00751-1
Alzheimer's disease: natural products as inhibitors of neuroinflammation
Abstract
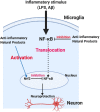
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and affects 44 million people worldwide. New emerging evidence from pre-clinical and clinical investigations shows that neuroinflammation is a major pathological component of AD suggesting that anti-inflammatory strategies are important in delaying the onset or slowing the progression of the disease. However, efforts to employ current anti-inflammatory agents in AD clinical trials have produced limited success. Consequently, there is a need to explore anti-inflammatory natural products, which target neuroinflammatory pathways relevant to AD pathogenesis. This review summarises important druggable molecular targets of neuroinflammation and presents classes of anti-neuroinflammatory natural products with potentials for preventing and reducing symptoms of AD.
Keywords: Alkaloids; Marine natural products; NF-κB; Polyphenols; Terpenes.
Figures


References
-
- Abulfadl YS, El-Maraghy NN, Ahmed AE, Nofal S, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Badary OA. Thymoquinone alleviates the experimentally induced Alzheimer's disease inflammation by modulation of TLRs signaling. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2018;37:1092–1104. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sung B. Pharmacological basis for the role of curcumin in chronic diseases: an age-old spice with modern targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad N, Ahmad R, Alam MA, Samim M, Iqbal Z, Ahmad FJ. Quantification and evaluation of thymoquinone loaded mucoadhesive nanoemulsion for treatment of cerebral ischemia. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;88:320–332. - PubMed
-
- Akhondzadeh S, Sabet MS, Harirchian MH, Togha M, Cheraghmakani H, Razeghi S, Hejazi SS, Yousefi MH, Alimardani R, Jamshidi A, Zare F, Moradi A. Saffron in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a 16-week, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010;35:581–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
