Clinical Characteristics of Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease-Related Retinopathy With CGG Repeat Expansions in the NOTCH2NLC Gene
- PMID: 32931575
- PMCID: PMC7500143
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.61.11.27
Clinical Characteristics of Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease-Related Retinopathy With CGG Repeat Expansions in the NOTCH2NLC Gene
Abstract
Purpose: To report the ocular characteristics of neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID)-related retinopathy with expansion of the CGG repeats in the NOTCH2NLC gene.
Methods: Seven patients from six families (aged 66-81 years) diagnosed with adult-onset NIID were studied. Ophthalmologic examinations, including the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), Goldmann perimetry, fundus photography, fundus autofluorescence (FAF) imaging, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and full-field electroretinography (ERGs), were performed. The expansion of the CGG repeats in the NOTCH2NLC gene was determined.
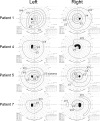
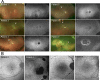
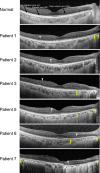
Results: All patients had an expansion of the CGG repeats (length approximately from 330-520 bp) in the NOTCH2NLC gene. The most common symptoms of the five symptomatic cases were reduced BCVA and night blindness. The other two cases did not have any ocular symptoms. The decimal BCVA varied from 0.15 to 1.2. Goldmann perimetry was constricted in all four cases tested; physiological blind spot was enlarged in two of the cases. The FAF images showed an absence of autofluorescence (AF) around the optic disc in all cases and also showed mild hypo-AF or extinguished AF in the midperiphery. In all cases, the OCT images showed an absence of the ellipsoid zone of the photoreceptors in the peripapillary region, and hyperreflective dots were also present between the retinal ganglion cell layer and outer nuclear layer. The macular region was involved in the late stage of the retinopathy. The full-field ERGs showed rod-cone dysfunction.
Conclusions: Patients with adult-onset NIID with CGG repeats expansions in the NOTCH2NLC gene had similar ophthalmologic features, including rod-cone dysfunction with progressive retinal degeneration in the peripapillary and midperipheral regions. The primary site is most likely the photoreceptors. Because the ocular symptoms are often overlooked due to dementia and occasionally precede the onset of dementia, detailed ophthalmological examinations are important for the early diagnosis of NIID-related retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Thdcr G. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell. 1993; 72: 971–983. - PubMed
-
- Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, et al. .. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991; 65: 905–914. - PubMed
-
- Orr HT, Chung MY, Banfi S, et al. .. Expansion of an unstable trinucleotide CAG repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Nat Genet. 1993; 4: 221–226. - PubMed
-
- Brook JD, McCurrach ME, Harley HG, et al. .. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992; 68: 799–808. - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Abe K, Aoki M, Itoyama Y, Tamai M. Ocular changes in patients with spinocerebellar degeneration and repeated trinucleotide expansion of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 gene. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115: 231–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

