NPC1 silent variant induces skipping of exon 11 (p.V562V) and unfolded protein response was found in a specific Niemann-Pick type C patient
- PMID: 32931663
- PMCID: PMC7667330
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1451
NPC1 silent variant induces skipping of exon 11 (p.V562V) and unfolded protein response was found in a specific Niemann-Pick type C patient
Abstract
Background: Niemann-Pick type C (NPC, MIM #257220) is a neuro-visceral disease, caused predominantly by pathogenic variants in the NPC1 gene. Here we studied patients with clinical diagnosis of NPC but inconclusive results regarding the molecular analysis.
Methods: We used a Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)-panel followed by cDNA analysis. Latter, we used massively parallel single-cell RNA-seq (MARS-Seq) to address gene profiling changes and finally the effect of different variants on the protein and cellular levels.
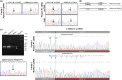
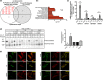
Results: We identified novel variants and cDNA analysis allowed us to establish the functional effect of a silent variant, previously reported as a polymorphism. We demonstrated that this variant induces the skipping of exon 11 leading to a premature stop codon and identified it in NPC patients from two unrelated families. MARS-Seq analysis showed that a number of upregulated genes were related to the unfolded protein response (UPR) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in one specific patient. Also, for all analyzed variants, the NPC1 protein was partially retained in the ER.
Conclusion: We showed that the NPC1 silent polymorphism (p.V562V) is a disease-causing variant in NPC and that the UPR is upregulated in an NPC patient.
Keywords: NPC1; Niemann-Pick type C; RNA-seq; exon skipping; silent variant; unfolded protein response.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigating p.Ala1035Val in NPC1: New Cellular Models for Niemann-Pick Type C Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 13;25(22):12186. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212186. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596250 Free PMC article.
-
New variants in Spanish Niemann-Pick type c disease patients.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Mar;47(3):2085-2095. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05308-7. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32060698
-
Variants in the Niemann-Pick type C gene NPC1 are not associated with Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2020 Sep;93:143.e1-143.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Neurobiol Aging. 2020. PMID: 32371106 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in the Definitive Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Type C-Leaky Variants and Alternative Transcripts.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;14(11):1990. doi: 10.3390/genes14111990. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pre-mRNA splicing defects and RNA binding protein involvement in Niemann Pick type C disease.J Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 20;318:20-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.03.012. Epub 2020 May 6. J Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32387451 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Profile, Putative Diagnostic Biomarkers and RNA-Based Therapies in the Inherited Lipid Storage Disease Niemann-Pick Type C.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 23;11(10):2615. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102615. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37892989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous Protein-Protein Interaction Network of the NPC Cholesterol Transporter 1 in the Cerebral Cortex.J Proteome Res. 2024 Aug 2;23(8):3174-3187. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00788. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 38686625 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPDC) by Mutation of NPC1 and NPC2: Aberrant Lysosomal Cholesterol Trafficking and Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;12(12):2021. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122021. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Aberrations Associated with the Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Cells. 2021 Sep 4;10(9):2317. doi: 10.3390/cells10092317. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe neurometabolic phenotype in npc1 -/- zebrafish with a C-terminal mutation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Mar 17;16:1078634. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1078634. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37008782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfalah, M. , Jacob, R. , & Naim, H. Y. (2002). Intestinal dipeptidyl peptidase IV is efficiently sorted to the apical membrane through the concerted action of N‐ and O‐glycans as well as association with lipid microdomains. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 10683–10690. 10.1074/jbc.M109357200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carter, M. S. , Doskow, J. , Morris, P. , Li, S. , Nhim, R. P. , Sandstedt, S. , & Wilkinson, M. F. (1995). A regulatory mechanism that detects premature nonsense codons in T‐cell receptor transcripts in vivo is reversed by protein synthesis inhibitors in vitro. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270, 28995–29003. 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28995 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

