Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19?
- PMID: 32931783
- PMCID: PMC7832734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551
Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19?
Abstract
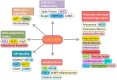
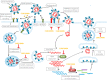
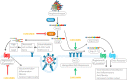
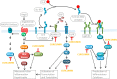
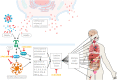
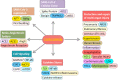
The severity of the recent pandemic and the absence of any specific medication impelled the identification of existing drugs with potential in the treatment of Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Curcumin, known for its pharmacological abilities especially as an anti-inflammatory agent, can be hypothesized as a potential candidate in the therapeutic regimen. COVID-19 has an assorted range of pathophysiological consequences, including pulmonary damage, elevated inflammatory response, coagulopathy, and multi-organ damage. This review summarizes the several evidences for the pharmacological benefits of curcumin in COVID-19-associated clinical manifestations. Curcumin can be appraised to hinder cellular entry, replication of SARS-CoV-2, and to prevent and repair COVID-19-associated damage of pneumocytes, renal cells, cardiomyocytes, hematopoietic stem cells, etc. The modulation and protective effect of curcumin on cytokine storm-related disorders are also discussed. Collectively, this review provides grounds for its clinical evaluation in the therapeutic management of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Curcumin; Cytokine storm; Inflammation; Molecular targets.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no competing interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Agrati C., Sacchi A., Bordoni V., Cimini E., Notari S., Grassi G., Casetti R., Tartaglia E., Lalle E., D'Abramo A. Expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Cell Death Differ. 2020:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0572-6. Advance online publication. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akinyemi A.J., Thome G.R., Morsch V.M., Stefanello N., Goularte J.F., Belló-Klein A., Oboh G., Schetinger M.R.C. Effect of dietary supplementation of ginger and turmeric rhizomes on angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) and arginase activities in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods. 2015;17:792–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.06.011. - DOI
-
- Almatroodi S.A., Alrumaihi F., Alsahli M.A., Alhommrani M.F., Khan A., Rahmani A.H. Curcumin, an active constituent of turmeric spice: implication in the prevention of lung injury induced by benzo(a) pyrene (BaP) in rats. Molecules. 2020;25(3):724. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

