Lactoferrin, a multi-functional glycoprotein: Active therapeutic, drug nanocarrier & targeting ligand
- PMID: 32932142
- PMCID: PMC7480805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120355
Lactoferrin, a multi-functional glycoprotein: Active therapeutic, drug nanocarrier & targeting ligand
Abstract
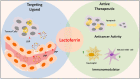
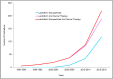
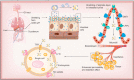
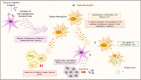
Recent progress in protein-based nanomedicine, inspired by the success of Abraxane® albumin-paclitaxel nanoparticles, have resulted in novel therapeutics used for treatment of challenging diseases like cancer and viral infections. However, absence of specific drug targeting, poor pharmacokinetics, premature drug release, and off-target toxicity are still formidable challenges in the clinic. Therefore, alternative protein-based nanomedicines were developed to overcome those challenges. In this regard, lactoferrin (Lf), a glycoprotein of transferrin family, offers a promising biodegradable well tolerated material that could be exploited both as an active therapeutic and drug nanocarrier. This review highlights the major pharmacological actions of Lf including anti-cancer, antiviral, and immunomodulatory actions. Delivery technologies of Lf to improve its pries and enhance its efficacy were also reviewed. Moreover, different nano-engineering strategies used for fabrication of drug-loaded Lf nanocarriers were discussed. In addition, the use of Lf for functionalization of drug nanocarriers with emphasis on tumor-targeted drug delivery was illustrated. Besides its wide application in oncology nano-therapeutics, we discussed the recent advances of Lf-based nanocarriers as efficient platforms for delivery of anti-parkinsonian, anti-Alzheimer, anti-viral drugs, immunomodulatory and bone engineering applications.
Keywords: Anti-viral drugs; Bone engineering; Cancer therapy; Drug delivery; Immunomodulatory functions; Lactoferrin; Nanoparticles; Tumor targeting.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Sorensen M.S. The Proteins in Whey, Whey. Compte rendu des Travaux du Laboratoire de Carlsberg Ser. Chim. 1939;23:55–99.
-
- Groves M.L. The isolation of a red protein from Milk2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960;82(13):3345–3350.
-
- Baker E.N., Lindley P.F. New perspectives on the structure and function of transferrins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1992;47(1):147–160. - PubMed
-
- Aboda A., Taha W., Attia I., Gad A., Mahmoud Mostafa M., Abdelfattah Abdelwadod M., Mohsen M., Kaur Kanwar R., Kanwar J.R. In: Advances and Avenues in the Development of Novel Carriers for Bioactives and Biological Agents. Singh M.R., Singh D., Kanwar J.R., Chauhan N.S., editors. Academic Press; 2020. Chapter 8 - iron bond bovine lactoferrin for the treatment of cancers and anemia associated with cancer cachexia; pp. 243–254.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

