Identification of Potential COX-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases Using Molecular Modeling Approaches
- PMID: 32932669
- PMCID: PMC7570943
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184183
Identification of Potential COX-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases Using Molecular Modeling Approaches
Abstract
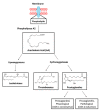
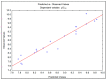
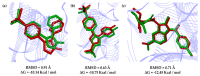
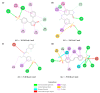
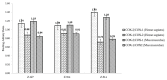
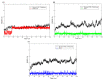
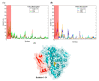
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) that were developed in order to avoid the side effects of non-selective inhibitors of COX-1. Thus, the present study aims to identify new selective chemical entities for the COX-2 enzyme via molecular modeling approaches. The best pharmacophore model was used to identify compounds within the ZINC database. The molecular properties were determined and selected with Pearson's correlation for the construction of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models to predict the biological activities of the compounds obtained with virtual screening. The pharmacokinetic/toxicological profiles of the compounds were determined, as well as the binding modes through molecular docking compared to commercial compounds (rofecoxib and celecoxib). The QSAR analysis showed a fit with R = 0.9617, R2 = 0.9250, standard error of estimate (SEE) = 0.2238, and F = 46.2739, with the tetra-parametric regression model. After the analysis, only three promising inhibitors were selected, Z-964, Z-627, and Z-814, with their predicted pIC50 (-log IC50) values, Z-814 = 7.9484, Z-627 = 9.3458, and Z-964 = 9.5272. All candidates inhibitors complied with Lipinski's rule of five, which predicts a good oral availability and can be used in in vitro and in vivo tests in the zebrafish model in order to confirm the obtained in silico data.
Keywords: COX-2 inhibitors; in silico; molecular modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


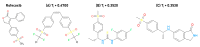



References
-
- Kim M.H., Son Y.-J., Lee S.Y., Yang W.S., Yi Y.-S., Yoon D.H., Yang Y., Kim S.H., Lee D., Rhee M.H., et al. JAK2-targeted anti-inflammatory effect of a resveratrol derivative 2,4-dihydroxy-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzamide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013;86:1747–1761. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Skinner B.W., Curtis K.A., Goodhart A.L. Hypnotics and Sedatives. In: Ray S., editor. Side Effects of Drugs Annual. Volume 40. Elsevier; Indianapolis, IN, USA: 2018. - DOI
-
- Bombardier C., Laine L., Reicin A., Shapiro D., Burgos-Vargas R., Davis B., Day R., Ferraz M.B., Hawkey C.J., Hochberg M.C., et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1520–1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011233432103. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

