Discovery of New Secondary Metabolites by Epigenetic Regulation and NMR Comparison from the Plant Endophytic Fungus Monosporascus eutypoides
- PMID: 32932749
- PMCID: PMC7570479
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184192
Discovery of New Secondary Metabolites by Epigenetic Regulation and NMR Comparison from the Plant Endophytic Fungus Monosporascus eutypoides
Abstract
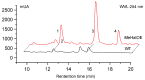
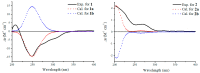
Overexpression of the histone acetyltransferase and the 1H NMR spectroscopic experiments of the endophytic fungus Monosporascus eutypoides resulted in the isolation of two new compounds, monosporasols A (1) and B (2), and two known compounds, pestaloficin C (3) and arthrinone (4). Their planar structures and absolute configurations were determined by spectroscopic analysis including high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (HRESIMS), one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) NMR, and calculated electronic circular dichroism data. Compounds 1-2 were screened in cytotoxic bioassays against HeLa, HCT-8, A549 and MCF-7 cells. Our work highlights the enormous potential of epigenetic manipulation along with the NMR comparison as an effective strategy for unlocking the chemical diversity encoded by fungal genomes.
Keywords: Monosporascus eutypoides; NMR comparison; cyclopropane derivatives; cytotoxic activities; epigenetic regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



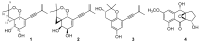


References
-
- Wu G., Zhou H., Zhang P., Wang X., Li W., Zhang W., Liu X., Liu H.-W., Keller N.P., An Z., et al. Polyketide production of pestaloficiols and macrodiolide ficiolides revealed by manipulations of epigenetic regulators in an endophytic fungus. Org. Lett. 2016;18:1832–1835. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00562. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

