Regulation of p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 Functions by Natural Polyphenols
- PMID: 32933137
- PMCID: PMC7564754
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10091316
Regulation of p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 Functions by Natural Polyphenols
Abstract
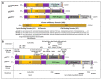
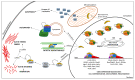
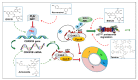
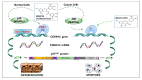
In numerous instances, the fate of a single cell not only represents its peculiar outcome but also contributes to the overall status of an organism. In turn, the cell division cycle and its control strongly influence cell destiny, playing a critical role in targeting it towards a specific phenotype. Several factors participate in the control of growth, and among them, p27Kip1 and p57Kip2, two proteins modulating various transitions of the cell cycle, appear to play key functions. In this review, the major features of p27 and p57 will be described, focusing, in particular, on their recently identified roles not directly correlated with cell cycle modulation. Then, their possible roles as molecular effectors of polyphenols' activities will be discussed. Polyphenols represent a large family of natural bioactive molecules that have been demonstrated to exhibit promising protective activities against several human diseases. Their use has also been proposed in association with classical therapies for improving their clinical effects and for diminishing their negative side activities. The importance of p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 in polyphenols' cellular effects will be discussed with the aim of identifying novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of important human diseases, such as cancers, characterized by an altered control of growth.
Keywords: EGCG; p27Kip1; p57Kip2; polyphenols; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) CDK inhibitors.Cell Cycle. 2010 Jun 15;9(12):2342-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.12.11988. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20519948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct developmental roles of cell cycle inhibitors p57Kip2 and p27Kip1 distinguish pituitary progenitor cell cycle exit from cell cycle reentry of differentiated cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(7):1895-908. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01885-08. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19139274 Free PMC article.
-
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57Kip2 regulates cell cycle exit, differentiation, and migration of embryonic cerebral cortical precursors.Cereb Cortex. 2011 Aug;21(8):1840-56. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq254. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Cereb Cortex. 2011. PMID: 21245411 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of the KIP family members p27(KIP1) and p57(KIP2) by SKP2 and the role of methylation in p57(KIP2) inactivation in nonsmall cell lung cancer.Int J Cancer. 2006 Dec 1;119(11):2546-56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22214. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16988944
-
p57KIP2: "Kip"ing the cell under control.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Dec;7(12):1902-19. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0317. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19934273 Review.
Cited by
-
p27Kip1, an Intrinsically Unstructured Protein with Scaffold Properties.Cells. 2021 Aug 31;10(9):2254. doi: 10.3390/cells10092254. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Cell Death Induced by Imine Analogs of Trans-Resveratrol: Induction of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Overproduction of Reactive Oxygen Species Leading to, or Not, Apoptosis without the Increase in the S-Phase of the Cell Cycle.Molecules. 2023 Apr 3;28(7):3178. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073178. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049947 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Genetic Conception of Obesity via the Dual Role of FoxO.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 20;22(6):3179. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063179. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p57Kip2 Phosphorylation Modulates Its Localization, Stability, and Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11176. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011176. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456957 Free PMC article.
-
5-Azacytidine Downregulates the Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting miR-139-5p/ROCK2 Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;14(7):1630. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071630. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406401 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

