Maternal N-Acetylcysteine Therapy Prevents Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Offspring: Implications of Hydrogen Sulfide-Generating Pathway and Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 32933169
- PMCID: PMC7554905
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9090856
Maternal N-Acetylcysteine Therapy Prevents Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Offspring: Implications of Hydrogen Sulfide-Generating Pathway and Gut Microbiota
Abstract
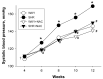
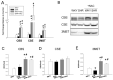
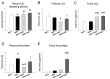
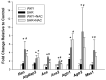
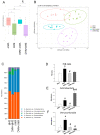
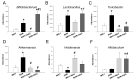
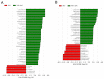
Hypertension can come from early life. N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) precursor as well as an antioxidant, has antihypertensive effect. We investigated whether maternal NAC therapy can protect spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) male offspring against hypertension. The pregnant rats were assigned to four groups: SHRs without treatment; Wistar Kyoto (WKY) without treatment; SHR+NAC, SHRs received 1% NAC in drinking water throughout pregnancy and lactation; and, WKY+NAC, WKY rats received 1% NAC in drinking water during pregnancy and lactation. Male offspring (n = 8/group) were killed at 12 weeks of age. Maternal NAC therapy prevented the rise in systolic blood pressure (BP) in male SHR offspring at 12 weeks of age. Renal cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulphurtransferase (3MST) protein levels and H2S-releasing activity were increased in the SHR+NAC offspring. Maternal NAC therapy increased fecal H2S and thiosulfate levels in the SHR+NAC group. Additionally, maternal NAC therapy differentially shaped gut microbiota and caused a distinct enterotype in each group. The protective effect of maternal NAC therapy against hypertension in SHR offspring is related to increased phylum Actinobacteria and genera Bifidobacterium and Allobaculum, but decreased phylum Verrucomicrobia, genera Turicibacter, and Akkermansia. Several microbes were identified as microbial markers, including genera Bifidobacterium, Allobaculum, Holdemania, and Turicibacter. Our results indicated that antioxidant therapy by NAC in pregnant SHRs can prevent the developmental programming of hypertension in male adult offspring. Our findings highlight the interrelationships among H2S-generating pathway in the kidneys and gut, gut microbiota, and hypertension. The implications of maternal NAC therapy elicited long-term protective effects on hypertension in later life that still await further clinical translation.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD); gut microbiota; hydrogen sulfide; hypertension; oxidative stress; renin-angiotensin system; thiosulfate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-Acetylcysteine Prevents Programmed Hypertension in Male Rat Offspring Born to Suramin-Treated Mothers.Biol Reprod. 2016 Jul;95(1):8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.139766. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Biol Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27251093
-
Maternal N-acetylcysteine therapy regulates hydrogen sulfide-generating pathway and prevents programmed hypertension in male offspring exposed to prenatal dexamethasone and postnatal high-fat diet.Nitric Oxide. 2016 Feb 29;53:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Nitric Oxide. 2016. PMID: 26743493
-
Early short-term treatment with exogenous hydrogen sulfide postpones the transition from prehypertension to hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rat.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018;40(1):58-64. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2017.1313847. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29072501
-
Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Sulfur Compounds on Kidney Health and Disease.Metabolites. 2023 May 25;13(6):688. doi: 10.3390/metabo13060688. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37367846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease: Hydrogen Sulfide as a Potential Target?Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 5;10(2):247. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020247. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Hypertension.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;12(2):281. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020281. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Erchen Decoction on Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 22;12:647529. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647529. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34366839 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiviral Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide by Blocking the Interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and Its Potential Cell Surface Receptors.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 3;2021:7866992. doi: 10.1155/2021/7866992. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34497683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combating hypertension beyond genome-wide association studies: Microbiome and artificial intelligence as opportunities for precision medicine.Camb Prism Precis Med. 2023 May 16;1:e26. doi: 10.1017/pcm.2023.13. eCollection 2023. Camb Prism Precis Med. 2023. PMID: 38550938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Role of Taurine on Rat Offspring Hypertension in the Setting of Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;12(12):2059. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122059. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136178 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

