Gradient boosting for Parkinson's disease diagnosis from voice recordings
- PMID: 32933493
- PMCID: PMC7493334
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-020-01250-7
Gradient boosting for Parkinson's disease diagnosis from voice recordings
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a clinically diagnosed neurodegenerative disorder that affects both motor and non-motor neural circuits. Speech deterioration (hypokinetic dysarthria) is a common symptom, which often presents early in the disease course. Machine learning can help movement disorders specialists improve their diagnostic accuracy using non-invasive and inexpensive voice recordings.
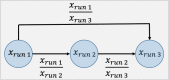
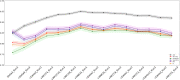
Method: We used "Parkinson Dataset with Replicated Acoustic Features Data Set" from the UCI-Machine Learning repository. The dataset included 44 speech-test based acoustic features from patients with PD and controls. We analyzed the data using various machine learning algorithms including Light and Extreme Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines, K-nearest neighborhood, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator Regression, as well as logistic regression. We also implemented a variable importance analysis to identify important variables classifying patients with PD.
Results: The cohort included a total of 80 subjects: 40 patients with PD (55% men) and 40 controls (67.5% men). Disease duration was 5 years or less for all subjects, with a mean Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) score of 19.6 (SD 8.1), and none were taking PD medication. The mean age for PD subjects and controls was 69.6 (SD 7.8) and 66.4 (SD 8.4), respectively. Our best-performing model used Light Gradient Boosting to provide an AUC of 0.951 with 95% confidence interval 0.946-0.955 in 4-fold cross validation using only seven acoustic features.
Conclusions: Machine learning can accurately detect Parkinson's disease using an inexpensive and non-invasive voice recording. Light Gradient Boosting outperformed other machine learning algorithms. Such approaches could be used to inexpensively screen large patient populations for Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Gradient boosting; Machine learning; Parkinson’s disease; Speech test.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has any conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimation of Parkinson's disease severity using speech features and extreme gradient boosting.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020 Nov;58(11):2757-2773. doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02250-5. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020. PMID: 32910301
-
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease based on voice signals using SHAP and hard voting ensemble method.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2024 Oct;27(13):1858-1874. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2023.2263125. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2024. PMID: 37771234
-
Non-invasive detection of Parkinson's disease based on speech analysis and interpretable machine learning.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Apr 30;17:1586273. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1586273. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40370753 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and wearable sensors for automated Parkinson's disease diagnosis aid: a systematic review.J Neurol. 2024 Oct;271(10):6452-6470. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12611-x. Epub 2024 Aug 14. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39143345
-
The role of AI and machine learning in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and atypical parkinsonisms.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2024 Sep;126:106986. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.106986. Epub 2024 May 3. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38724317 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Parkinson's Disease and Its Pathology via Simple Clinical Variables.J Parkinsons Dis. 2022;12(1):341-351. doi: 10.3233/JPD-212876. J Parkinsons Dis. 2022. PMID: 34602502 Free PMC article.
-
PD-DETECTOR: A sustainable and computationally intelligent mobile application model for Parkinson's disease severity assessment.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 15;10(14):e34593. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34593. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39130458 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning model for predicting immediate postoperative desaturation using spirometry signal data.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 11;13(1):21881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49062-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38072984 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the risk of developing end-stage renal diseases in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus using artificial intelligence algorithms.BioData Min. 2023 Mar 10;16(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13040-023-00324-2. BioData Min. 2023. PMID: 36899426 Free PMC article.
-
Light gradient boost tree classifier predictions on appendicitis with periodontal disease from biochemical and clinical parameters.Front Oral Health. 2024 Sep 13;5:1462873. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1462873. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39346113 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical