Mitochondrial DNA copy number and incident atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 32933497
- PMCID: PMC7493408
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-020-01715-6
Mitochondrial DNA copy number and incident atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Mechanistic studies suggest that mitochondria DNA (mtDNA) dysfunction may be associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation (AF). The association between mtDNA copy number (mtDNA-CN) and incident AF in the general population, however, remains unknown.
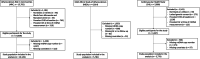
Methods: We conducted prospective analyses of 19,709 participants from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study (ARIC), the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), and the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS). mtDNA-CN from the peripheral blood was calculated from probe intensities on the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) Array 6.0 in ARIC and MESA and from multiplexed real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) in CHS. Incident AF cases were identified through electrocardiograms, review of hospital discharge codes, Medicare claims, and death certificates.
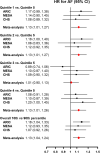
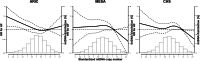
Results: The median follow-up time was 21.4 years in ARIC, 12.9 years in MESA, and 11.0 years in CHS, during which 4021 participants developed incident atrial fibrillation (1761 in ARIC, 790 in MESA, and 1470 in CHS). In fully adjusted models, participants with the lowest quintile of mitochondria DNA copy number had an overall 13% increased risk (95% CI 1 to 27%) of incident atrial fibrillation compared to those with the highest quintile. Dose-response spline analysis also showed an inverse association between mitochondria DNA copy number and hazard for atrial fibrillation for all three cohorts. These associations were consistent across subgroups.
Conclusions: Mitochondria DNA copy number was inversely associated with the risk of AF independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. These findings implicate mitochondria DNA copy number as a novel risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Further research is warranted to understand the underlying mechanisms and to evaluate the role of mitochondria DNA copy number in the management of atrial fibrillation risk.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Mitochondria DNA copy number; mtDNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mou L, Norby FL, Chen LY, O’Neal WT, Lewis TT, Loehr LR, Soliman EZ, Alonso A. Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation by race and socioeconomic status: ARIC Study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018;11(7):e006350. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.118.006350. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum RF, Kim YH, McAnulty JH, Jr, Zheng ZJ, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 2014;129(8):837–847. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 16EIA26410001/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111089/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL148521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL137259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131573/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141989/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127659/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

