RACE-trial: neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy versus chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced, potentially resectable adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction - a randomized phase III joint study of the AIO, ARO and DGAV
- PMID: 32933498
- PMCID: PMC7493344
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07388-x
RACE-trial: neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy versus chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced, potentially resectable adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction - a randomized phase III joint study of the AIO, ARO and DGAV
Abstract
Background: Despite obvious advances over the last decades, locally advanced adenocarcinomas of the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) still carry a dismal prognosis with overall 5-year survival rates of less than 50% even when using modern optimized treatment protocols such as perioperative chemotherapy based on the FLOT regimen or radiochemotherapy. Therefore the question remains whether neoadjuvant chemotherapy or neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy is eliciting the best results in patients with GEJ cancer. Hence, an adequately powered multicentre trial comparing both therapeutic strategies is clearly warranted.
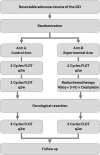
Methods: The RACE trial is a an investigator initiated multicenter, prospective, randomized, stratified phase III clinical trial and seeks to investigate the role of preoperative induction chemotherapy (2 cycles of FLOT: 5-FU, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, docetaxel) with subsequent preoperative radiochemotherapy (oxaliplatin weekly, 5-FU plus concurrent fractioned radiotherapy to a dose of 45 Gy) compared to preoperative chemotherapy alone (4 cycles of FLOT), both followed by resection and postoperative completion of chemotherapy (4 cycles of FLOT), in the treatment of locally advanced, potentially resectable adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction. Patients with cT3-4, any N, M0 or cT2 N+, M0 adenocarcinoma of the GEJ are eligible for inclusion. The RACE trial aims to enrol 340 patients to be allocated to both treatment arms in a 1:1 ratio stratified by tumour site. The primary endpoint of the trial is progression-free survival assessed with follow-up of maximum 60 months. Secondary endpoints include overall survival, R0 resection rate, number of harvested lymph nodes, site of tumour relapse, perioperative morbidity and mortality, safety and toxicity and quality of life.
Discussion: The RACE trial compares induction chemotherapy with FLOT followed by preoperative oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil-based chemoradiation versus preoperative chemotherapy with FLOT alone, both followed by surgery and postoperative completion of FLOT chemotherapy in the treatment of locally advanced, non-metastatic adenocarcinoma of the GEJ. The trial aims to show superiority of the combined chemotherapy/radiochemotherapy treatment, assessed by progression-free survival, over perioperative chemotherapy alone.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov ; NCT04375605 ; Registered 4th May 2020.
Keywords: FLOT; Locally advanced adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction; Neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy; Perioperative chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perioperative treatment in resectable gastric cancer with spartalizumab in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and docetaxel (FLOT): a phase II study (GASPAR).BMC Cancer. 2022 May 12;22(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09623-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35549674 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Histopathological regression after neoadjuvant docetaxel, oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil or capecitabine in patients with resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4-AIO): results from the phase 2 part of a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2/3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Dec;17(12):1697-1708. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30531-9. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27776843 Clinical Trial.
-
Preventive HIPEC in combination with perioperative FLOT versus FLOT alone for resectable diffuse type gastric and gastroesophageal junction type II/III adenocarcinoma - the phase III "PREVENT"- (FLOT9) trial of the AIO /CAOGI /ACO.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 29;21(1):1158. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08872-8. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34715810 Free PMC article.
-
FLOT or CROSS for gastroesophageal junction cancers-is the debate over yet?Chin Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun;12(3):24. doi: 10.21037/cco-23-5. Epub 2023 May 25. Chin Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37303220 Review.
-
The Role of Systemic Therapy in Resectable Gastric and Gastro-oesophageal Junction Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Nov 16;18(12):69. doi: 10.1007/s11864-017-0510-0. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29143893 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncological recurrence following pathological complete response after neoadjuvant treatment in patients with esophageal cancer - a retrospective cohort study.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Sep 18;408(1):363. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-03100-2. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 37721586 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Therapy of Upper Gastrointestinal Malignancies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 14;13(4):793. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040793. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672858 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Current status and future perspectives for the treatment of resectable locally advanced esophagogastric junction cancer: A narrative review.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 28;29(24):3758-3769. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3758. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37426325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of Tumor Regression Grade After Chemotherapy Versus Chemoradiotherapy in Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Treatment for Locally Advanced Esophageal Adenocarcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug;32(8):5909-5918. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-17264-2. Epub 2025 May 5. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40323553 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative chemotherapy with 5-FU, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel (FLOT) for esophagogastric adenocarcinoma: ten years real-life experience from a surgical perspective.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Feb 10;408(1):81. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-02822-7. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 36763220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mönig S, Ott K, Gockel I, Lorenz D, Ludwig K, Messmann H, et al. S3 guidelines on gastric cancer-diagnosis and treatment of adenocarcinoma of the stomach and esophagogastric junction : version 2.0-august 2019. AWMF register number: 032/009OL. Chirurg. 2020;91(1):37–40. doi: 10.1007/s00104-020-01112-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

