Systematic genetic and proteomic screens during gametogenesis identify H2BK34 methylation as an evolutionary conserved meiotic mark
- PMID: 32933557
- PMCID: PMC7493871
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-020-00349-5
Systematic genetic and proteomic screens during gametogenesis identify H2BK34 methylation as an evolutionary conserved meiotic mark
Abstract
Background: Gametes are highly differentiated cells specialized to carry and protect the parental genetic information. During male germ cell maturation, histone proteins undergo distinct changes that result in a highly compacted chromatin organization. Technical difficulties exclude comprehensive analysis of precise histone mutations during mammalian spermatogenesis. The model organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae possesses a differentiation pathway termed sporulation which exhibits striking similarities to mammalian spermatogenesis. This study took advantage of this yeast pathway to first perform systematic mutational and proteomics screens on histones, revealing amino acid residues which are essential for the formation of spores.
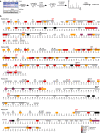
Methods: A systematic mutational screen has been performed on the histones H2A and H2B, generating ~ 250 mutants using two genetic backgrounds and assessing their ability to form spores. In addition, histones were purified at key stages of sporulation and post-translational modifications analyzed by mass spectrometry.
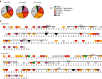
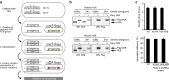
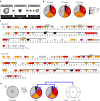
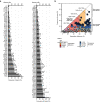
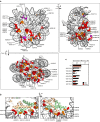
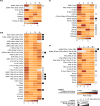
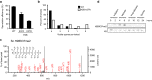
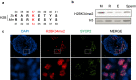
Results: The mutation of 75 H2A H2B residues affected sporulation, many of which were localized to the nucleosome lateral surface. The use of different genetic backgrounds confirmed the importance of many of the residues, as 48% of yeast histone mutants exhibited impaired formation of spores in both genetic backgrounds. Extensive proteomic analysis identified 67 unique post-translational modifications during sporulation, 27 of which were previously unreported in yeast. Furthermore, 33 modifications are located on residues that were found to be essential for efficient sporulation in our genetic mutation screens. The quantitative analysis of these modifications revealed a massive deacetylation of all core histones during the pre-meiotic phase and a close interplay between H4 acetylation and methylation during yeast sporulation. Methylation of H2BK37 was also identified as a new histone marker of meiosis and the mouse paralog, H2BK34, was also enriched for methylation during meiosis in the testes, establishing conservation during mammalian spermatogenesis.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that a combination of genetic and proteomic approaches applied to yeast sporulation can reveal new aspects of chromatin signaling pathways during mammalian spermatogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic screen reveals new functional dynamics of histones H3 and H4 during gametogenesis.Genes Dev. 2010 Aug 15;24(16):1772-86. doi: 10.1101/gad.1954910. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20713519 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of histone H4 Ser1 regulates sporulation in yeast and is conserved in fly and mouse spermatogenesis.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 15;20(18):2580-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.1457006. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16980586 Free PMC article.
-
The linker histone plays a dual role during gametogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul;32(14):2771-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00282-12. Epub 2012 May 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22586276 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling in yeast sporulation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Jun 27;306(2):325-8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00983-5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12804565 Review.
-
Choose Your Own Adventure: The Role of Histone Modifications in Yeast Cell Fate.J Mol Biol. 2017 Jun 30;429(13):1946-1957. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27769718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review of the current status.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Feb 24;21:1843-1850. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.02.037. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36915383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paf1 complex subunit Rtf1 stimulates H2B ubiquitylation by interacting with the highly conserved N-terminal helix of Rad6.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 May 30;120(22):e2220041120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220041120. Epub 2023 May 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37216505 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Histone H3 Modifications Regulate Meiosis Initiation via Respiration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:646214. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646214. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrell DT, Hammoud SS. The human sperm epigenome and its potential role in embryonic development. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010;16:37–47. - PubMed
-
- Carrell DT. Epigenetics of the male gamete. Fertil Steril. 2012;97:267–274. - PubMed
-
- Gannon JR, Emery BR, Jenkins TG, Carrell DT. The sperm epigenome: implications for the embryo. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;791:53–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

