Chloroquine Sensitizes GNAQ/11-mutated Melanoma to MEK1/2 Inhibition
- PMID: 32933997
- PMCID: PMC7710560
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1675
Chloroquine Sensitizes GNAQ/11-mutated Melanoma to MEK1/2 Inhibition
Abstract
Purpose: Mutational activation of GNAQ or GNA11 (GNAQ/11), detected in >90% of uveal melanomas, leads to constitutive activation of oncogenic pathways, including MAPK and YAP. To date, chemo- or pathway-targeted therapies, either alone or in combination, have proven ineffective in the treatment of patients with metastatic uveal melanoma.
Experimental design: We tested the efficacy of chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine, in combination with MAPK pathway inhibition in GNAQ/11-mutated cells in vitro and in vivo and identified mechanisms of MEK1/2 inhibitor plus chloroquine-induced cytotoxicity.
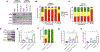
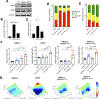
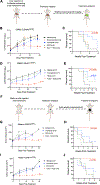
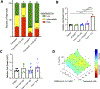
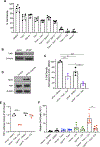
Results: Inhibition of GNAQ/11-mediated activation of MAPK signaling resulted in the induction of autophagy. Combined inhibition of Gα and autophagy or lysosome function resulted in enhanced cell death. Moreover, the combination of MEK1/2 inhibition, using trametinib, with the lysosome inhibitor, chloroquine, also increased cytotoxicity. Treatment of mice bearing GNAQ/11-driven melanomas with trametinib plus hydroxychloroquine resulted in inhibition of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. Interestingly, lysosomal- and autophagy-specific inhibition with bafilomycin A1 was not sufficient to promote cytotoxicity in combination with trametinib. However, the addition of YAP inhibition with trametinib plus bafilomycin A1 resulted in cell death at comparable levels to trametinib plus chloroquine (T/CQ) treatment. Furthermore, T/CQ-treated cells displayed decreased YAP nuclear localization and decreased YAP transcriptional activity. Expression of a constitutively active YAP5SA mutant conferred resistance to T/CQ-induced cell death.
Conclusions: These results suggest that YAP, MEK1/2, and lysosome function are necessary and critical targets for the therapy of GNAQ/11-driven melanoma, and identify trametinib plus hydroxychloroquine as a potential treatment strategy for metastatic uveal melanoma.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
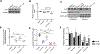
Similar articles
-
Combination small molecule MEK and PI3K inhibition enhances uveal melanoma cell death in a mutant GNAQ- and GNA11-dependent manner.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 15;18(16):4345-55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3227. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22733540 Free PMC article.
-
Combined PKC and MEK inhibition in uveal melanoma with GNAQ and GNA11 mutations.Oncogene. 2014 Sep 25;33(39):4724-34. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.418. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24141786 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase α selective inhibitor BYL719 enhances the effect of the protein kinase C inhibitor AEB071 in GNAQ/GNA11-mutant uveal melanoma cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(5):1044-53. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0550. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24563540 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GNAQ/11 through PKC inhibition in uveal melanoma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2022 Dec;29(12):1809-1813. doi: 10.1038/s41417-022-00437-6. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 35181742 Review.
-
GNAQ and GNA11 mutations in uveal melanoma.Melanoma Res. 2014 Dec;24(6):525-34. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000121. Melanoma Res. 2014. PMID: 25304237 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-Treatment of Chloroquine and Trametinib Inhibits Melanoma Cell Proliferation and Decreases Immune Cell Infiltration.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:782877. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.782877. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847840 Free PMC article.
-
Elaiophylin Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Human Uveal Melanoma by Suppressing Mitophagy and Inducing Oxidative Stress via Modulating SIRT1/FoxO3a Signaling.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 21;12:788496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.788496. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35387119 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic rewiring directs melanoma immunology.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 8;13:909580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.909580. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36003368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Immune Cell Infiltration Landscape and Their Prognostic Significance in Uveal Melanoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 26;9:713569. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.713569. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513843 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition Effect of Chloroquine and Integrin-Linked Kinase Knockdown on Translation in Melanoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 1;22(7):3682. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073682. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33916175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kujala E, Makitie T, Kivela T. Very long-term prognosis of patients with malignant uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44(11):4651–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

