Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 32934047
- PMCID: PMC7539730
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0696
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
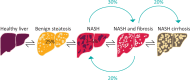
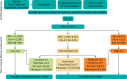
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. NAFLD is defined by excess fat in the liver and has a multidirectional relationship with metabolic syndrome. The prevalence of NAFLD has risen rapidly in recent years in line with the obesity epidemic and associated increases in type 2 diabetes, hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia. Patients with NAFLD are at risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and in a proportion of individuals, NAFLD is associated with liver damage. This article summarises the epidemiology of NAFLD, the clinical approach to risk-assessing patients and briefly outlines current and future management options.
Keywords: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; cirrhosis; fibrosis; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
© Royal College of Physicians 2020. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms, screening modalities and treatment options for individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes.Diabet Med. 2020 Nov;37(11):1793-1806. doi: 10.1111/dme.14356. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Diabet Med. 2020. PMID: 32619031 Review.
-
Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030.J Hepatol. 2018 Oct;69(4):896-904. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29886156
-
Clinical outcomes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Polish-case control study.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Dec;28(12):1615-1620. doi: 10.17219/acem/106173. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31025557
-
Prevalence and Predictors of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Morbidly Obese South Indian Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery.Obes Surg. 2015 Nov;25(11):2078-87. doi: 10.1007/s11695-015-1655-1. Obes Surg. 2015. PMID: 25835982
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the liver disease of our age?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9072-89. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9072. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Peptides from Miiuy Croaker Swim Bladders: Ameliorating Effect and Mechanism in NAFLD Cell Model through Regulation of Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Capacity.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 1;23(2):63. doi: 10.3390/md23020063. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997187 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine-β-muricholic acid antagonizes the intestinal farnesoid X receptor-ceramide axis and ameliorates NASH in mice.Hepatol Commun. 2022 Dec;6(12):3363-3378. doi: 10.1002/hep4.2099. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Hepatol Commun. 2022. PMID: 36196594 Free PMC article.
-
Spheroid Engineering in Microfluidic Devices.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 18;8(4):3630-3649. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06052. eCollection 2023 Jan 31. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36743071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory markers as predictors of liver fibrosis in type 2 diabetes patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 8;16:1556646. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1556646. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40265164 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Strategies in Enhancing the Hepatoprotective Efficacy of Natural Products: Integrating Nanotechnology, Genomics, and Mechanistic Insights.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 May 12;11(5):2528-2549. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00004. Epub 2025 Apr 11. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40211874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J, International Consensus Panel MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020;158:1999–2014.e1. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – A global public health perspective. J Hepatol 2019;70:531–44. - PubMed
-
- Bril F, Cusi K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2016;45:765–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

