Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 32934047
- PMCID: PMC7539730
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0696
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
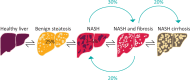
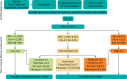
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. NAFLD is defined by excess fat in the liver and has a multidirectional relationship with metabolic syndrome. The prevalence of NAFLD has risen rapidly in recent years in line with the obesity epidemic and associated increases in type 2 diabetes, hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia. Patients with NAFLD are at risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and in a proportion of individuals, NAFLD is associated with liver damage. This article summarises the epidemiology of NAFLD, the clinical approach to risk-assessing patients and briefly outlines current and future management options.
Keywords: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; cirrhosis; fibrosis; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
© Royal College of Physicians 2020. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J, International Consensus Panel MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020;158:1999–2014.e1. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – A global public health perspective. J Hepatol 2019;70:531–44. - PubMed
-
- Bril F, Cusi K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2016;45:765–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

