Pharmacophore hybridisation and nanoscale assembly to discover self-delivering lysosomotropic new-chemical entities for cancer therapy
- PMID: 32934241
- PMCID: PMC7493904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18399-4
Pharmacophore hybridisation and nanoscale assembly to discover self-delivering lysosomotropic new-chemical entities for cancer therapy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Pharmacophore hybridisation and nanoscale assembly to discover self-delivering lysosomotropic new-chemical entities for cancer therapy.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 25;12(1):2013. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22419-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33767181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
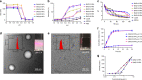
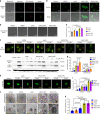
Integration of the unique advantages of the fields of drug discovery and drug delivery is invaluable for the advancement of drug development. Here we propose a self-delivering one-component new-chemical-entity nanomedicine (ONN) strategy to improve cancer therapy through incorporation of the self-assembly principle into drug design. A lysosomotropic detergent (MSDH) and an autophagy inhibitor (Lys05) are hybridised to develop bisaminoquinoline derivatives that can intrinsically form nanoassemblies. The selected BAQ12 and BAQ13 ONNs are highly effective in inducing lysosomal disruption, lysosomal dysfunction and autophagy blockade and exhibit 30-fold higher antiproliferative activity than hydroxychloroquine used in clinical trials. These single-drug nanoparticles demonstrate excellent pharmacokinetic and toxicological profiles and dramatic antitumour efficacy in vivo. In addition, they are able to encapsulate and deliver additional drugs to tumour sites and are thus promising agents for autophagy inhibition-based combination therapy. Given their transdisciplinary advantages, these BAQ ONNs have enormous potential to improve cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.L. and Z.M. are the co-inventors on a pending patent application on the hybrid compounds and the resulting nanoformulations. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Qin SY, Zhang AQ, Cheng SX, Rong L, Zhang XZ. Drug self-delivery systems for cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2017;112:234–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

