Blood myo-inositol concentrations in preterm and term infants
- PMID: 32934363
- PMCID: PMC7889639
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-020-00799-5
Blood myo-inositol concentrations in preterm and term infants
Abstract
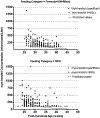
Objective: To describe relationship between cord blood (representing fetal) myo-inositol concentrations and gestational age (GA) and to determine trends of blood concentrations in enterally and parenterally fed infants from birth to 70 days of age.
Design/methods: Samples were collected in 281 fed or unfed infants born in 2005 and 2006. Myo-inositol concentrations were displayed in scatter plots and analyzed with linear regression models of natural log-transformed values.
Results: In 441 samples obtained from 281 infants, myo-inositol concentrations varied from nondetectable to 1494 μmol/L. Cord myo-inositol concentrations decreased an estimated 11.9% per week increase in GA. Postnatal myo-inositol concentrations decreased an estimated 14.3% per week increase in postmenstrual age (PMA) and were higher for enterally fed infants compared to unfed infants (51% increase for fed vs. unfed infants).
Conclusions: Fetal myo-inositol concentrations decreased with increasing GA. Postnatal concentrations decreased with increasing PMA and were higher among enterally fed than unfed infants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hallman M Inositol during perinatal transition. Neo Reviews. 2015;16:e84.
-
- Carver JD, Stromquist CI, Benford VJ, Minervini G, Benford SA, Barness LA. Postnatal inositol levels in preterm infants. J Perinatol. 1997;17:389–92. - PubMed
-
- Brusati V, Józwik M, Józwik M, Teng C, Paolini C, Marconi AM, et al. Fetal and maternal non-glucose carbohydrates and polyols concentrations in normal human pregnancies at term. Pediatr Res. 2005;58:700–4. - PubMed
-
- Pereira GR, Baker L, Egler J, Corcoran L, Chiacacci R. Serum myo-inositol concentrations in premature infants fed human milk, formula for infants, and parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51:589–93. - PubMed
-
- Cavalli C, Teng C, Battaglia FC, Bevilacqua G. Free sugar and sugar alcohol concentrations in human breast milk. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;42:215–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD037261/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD046000/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD045993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD045986/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD037249/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD095254/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

