Comparative evaluation of oral melatonin and oral clonidine for the attenuation of haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation-A prospective randomised double blind study
- PMID: 32934404
- PMCID: PMC7457986
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_76_20
Comparative evaluation of oral melatonin and oral clonidine for the attenuation of haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation-A prospective randomised double blind study
Abstract
Background and aims: Laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation cause significant derangement of the haemodynamic parameters proving detrimental for some patients. Clonidine, an α-2 adrenoreceptor agonist, and melatonin, the pineal hormone, have been used for the attenuation of these haemodynamic responses. This study was designed to evaluate the effect of oral melatonin and clonidine in attenuating the haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation.
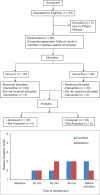
Materials and methods: In this prospective randomised double-blind study, 60 American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) grade I and II patients aged 20-60 years of either gender scheduled to undergo elective surgery under general anaesthesia were randomly divided into Group M and Group C and orally received 6 mg of melatonin and 0.2 mg of clonidine, respectively, 120 min before the induction of anaesthesia. The haemodynamic parameters-heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure and rate -pressure product(RPP) were recorded before and 120 min after the administration of the study drug, before induction, immediately after intubation and at 1, 3, 5 and 10 min following intubation. Sedation was assessed using the Ramsay Sedation Scale. The qualitative and quantitative variables were analysed using Chi square test and unpaired student t test, respectively. For intragroup comparison of quantitative data, paired t test was applied. A P value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results: A significant difference was noted between the groups regarding HR and RPP 0, 1, 3 and 5 min after intubation. The Ramsay sedation score ranged between 2 and 3 at all time intervals.
Conclusion: Although both the drugs are effective, oral melatonin proved superior to oral clonidine in attenuating the haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation without any side effects.
Keywords: Clonidine; endotracheal intubation; haemodynamic; laryngoscopy; melatonin.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of melatonin in attenuation of haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation.Indian J Anaesth. 2016 Oct;60(10):712-718. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.191667. Indian J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27761033 Free PMC article.
-
Oral clonidine for attenuation of haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation in known hypertensive patients.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2012 Jul-Dec;24(3-4):174-6. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2012. PMID: 24669646 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral Clonidine vs Oral Pregabalin Premedication to Attenuate Pressor Response to Direct Laryngoscopy in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Double Blind Study.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Sep;10(9):UC21-UC25. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/19756.8513. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27790557 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Oral Clonidine and Gabapentin Premedication for Attenuation of Pressor Response to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation.Anesth Essays Res. 2020 Jul-Sep;14(3):412-419. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_114_20. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Anesth Essays Res. 2020. PMID: 34092851 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of the pressor response to direct laryngoscopy and tracheal Intubation: oral clonidine vs. oral gabapentin premedication.J Res Med Sci. 2011 Mar;16 Suppl 1(Suppl1):S377-86. J Res Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22247722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of hypotensive properties of dexmedetomidine versus clonidine for induced hypotension during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: A randomised, double-blind interventional study.Indian J Anaesth. 2021 Aug;65(8):579-585. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_57_21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Indian J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 34584280 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of oral melatonin premedication on hemodynamic responses to intubation, anesthetic requirements and postoperative sedation: A randomized trial.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Oct-Dec;39(4):596-602. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_159_22. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38269180 Free PMC article.
-
Role of melatonin in attenuation of hemodynamic response to intubation and anesthetic requirements: a randomized, controlled, double-blind study.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023 Jul-Aug;73(4):434-440. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2021.08.011. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 34560112 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Henderson JN, Miller RD. Airway management in the adult I. Miller×s Anaesthesia. 2010:1573–1610.
-
- Koti VR, Cheuri SB, Pulla S, Varunchander G. Attenuation of haemodynamic response to intubation with oral clonidine and oral atenolol. Indian J Clin Anaesth. 2016;3:251–56.
-
- Ugur B, Ogurlu M, Gursoy F. Effects of esmolol, lidocaine and fentanyl on haemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation. Clin Drug Investig. 2007;27:269–77. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan L, Kaur M, Gupta R, Aujla KS, Singh A, Kaur A. Attenuation of the pressor responses to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation with intravenous dexmedetomidine versus magnesium sulphate under bispectral index-controlled anaesthesia: A placebo-controlled prospective randomised trial. Indian J Anaesth. 2018;62:337–43. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources