A novel monoclonal antibody against human B7-1 protects against chronic graft-vs.-host disease in a murine lupus nephritis model
- PMID: 32934679
- PMCID: PMC7471967
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9146
A novel monoclonal antibody against human B7-1 protects against chronic graft-vs.-host disease in a murine lupus nephritis model
Abstract
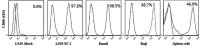
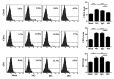
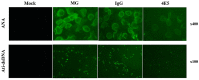
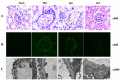
Lupus nephritis (LN) is the most common complication that causes mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The B7-1/B7-2 and CD28/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 co-stimulatory pathway serves a key role in autoimmune disease and organ transplantation. The aim of the present study was to generate and characterize a monoclonal antibody (mAb; clone 4E5) against human B7-1 and to investigate its potential use for the treatment of LN. The results demonstrated that the 4E5 mAb was successfully generated and able to recognize both human and mouse B7-1. After injection of this mAb into a mouse model with chronic graft-vs.-host disease (cGVHD)-induced lupus-like disease, the expression of CD21, CD23, CD80 and CD86 on B220+ B-cells in the spleen, and the concentrations of serum autoantibodies and urine protein, were decreased. Direct immunofluorescence analysis of the kidneys revealed that immunofluorescence of immune complex deposits was weaker in the 4E5-treated mice and electron microscopy analyses of renal tissues indicated that pathological injury of the kidneys of 4E5-treated mice was decreased compared with that in the model control mice. The results of the present study demonstrated that inhibition of the B7-1/CD28 co-stimulatory signaling pathway with the 4E5 mAb may represent a promising strategy to decelerate the progression of LN that is induced by cGVHD with potential for use in the treatment of other autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: anti-human B7-1 antibody; autoantibodies; chronic graft-vs.-host disease; electron microscopy; lupus nephritis.
Copyright: © Shen et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A monoclonal antibody against CD86 and its protection in a murine lupus nephritis model of chronic graft-versus-host disease.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2017 Oct;39(5):285-291. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2017.1354878. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2017. PMID: 28747139
-
Reducing progression of experimental lupus nephritis via inhibition of the B7/CD28 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4187-4195. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3953. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26096149 Free PMC article.
-
A novel monoclonal antibody against human CD80 and its immune protection in a mouse lupus-like disease.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011 Jul-Sep;24(3):583-93. doi: 10.1177/039463201102400304. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21978690
-
Preferential dependence of autoantibody production in murine lupus on CD86 costimulatory molecule.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Nov;25(11):3060-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251112. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7489744
-
Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.225. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244036 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
